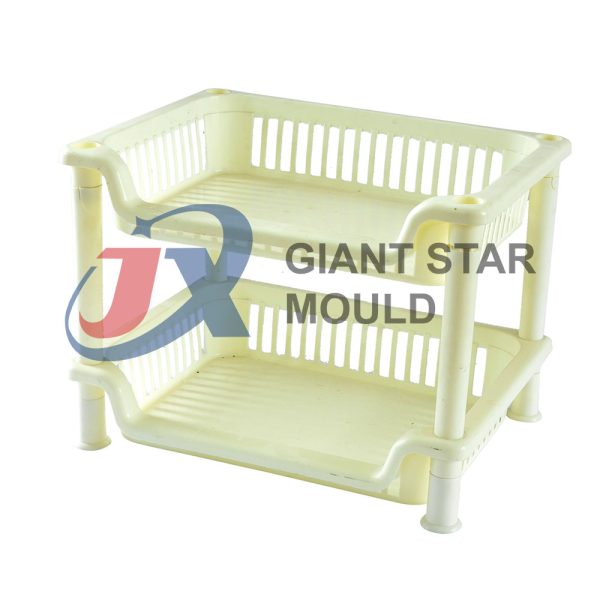
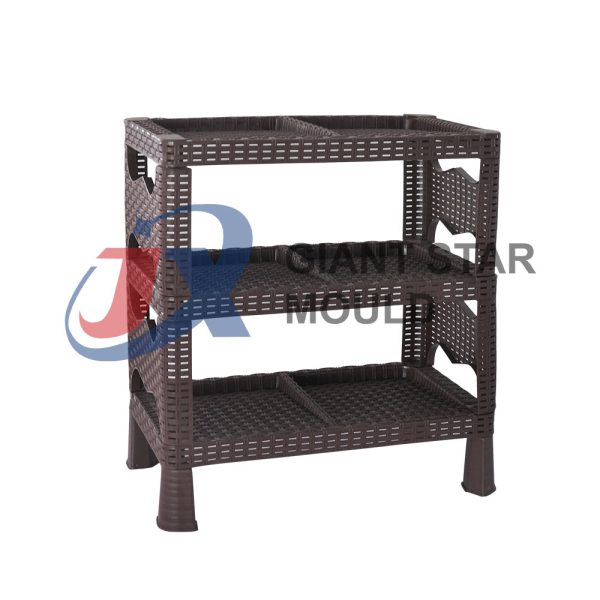
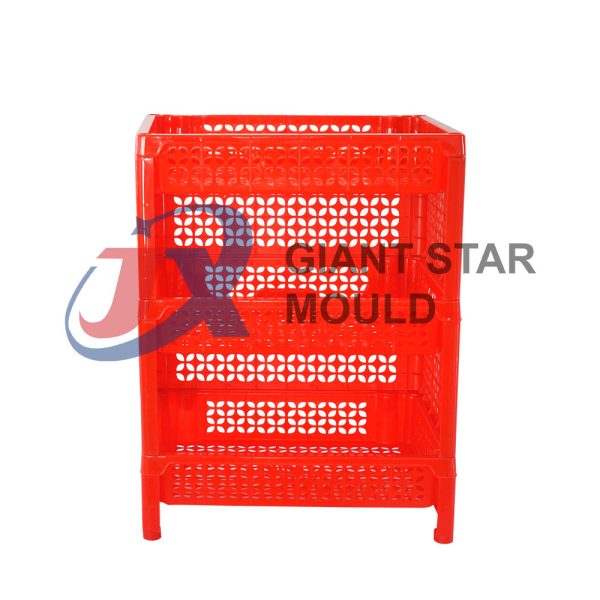
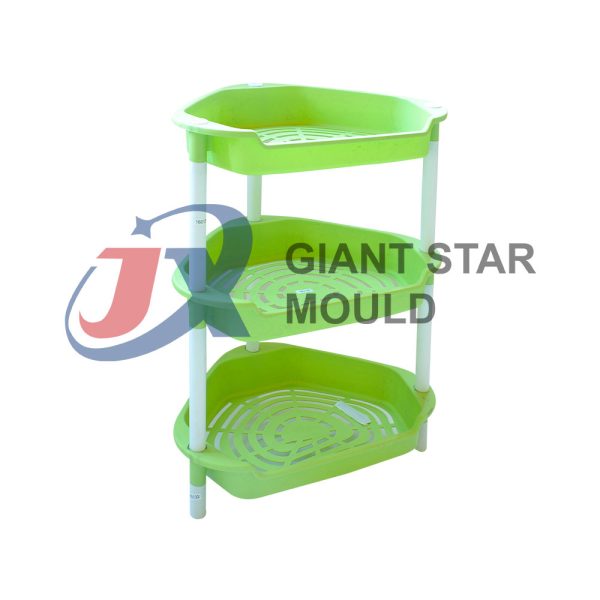
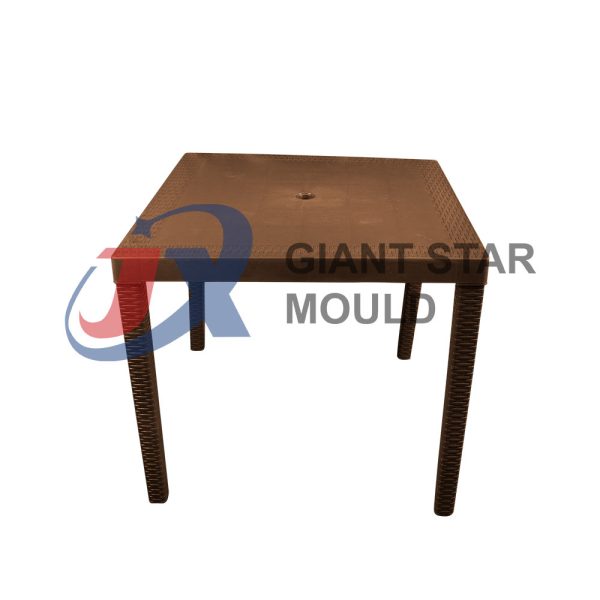
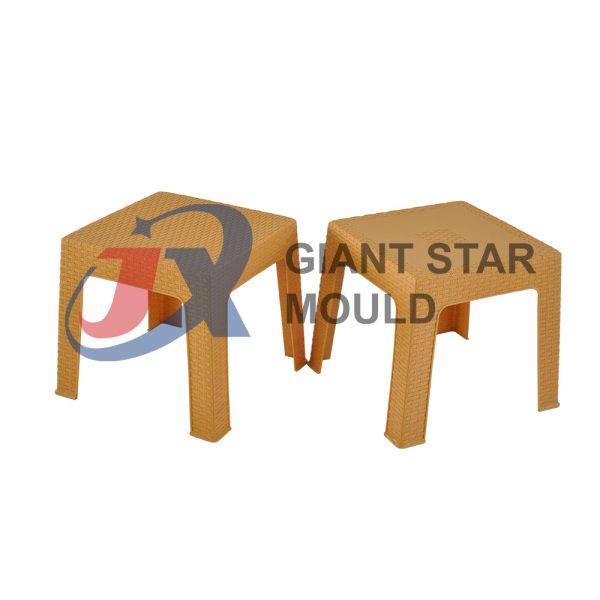
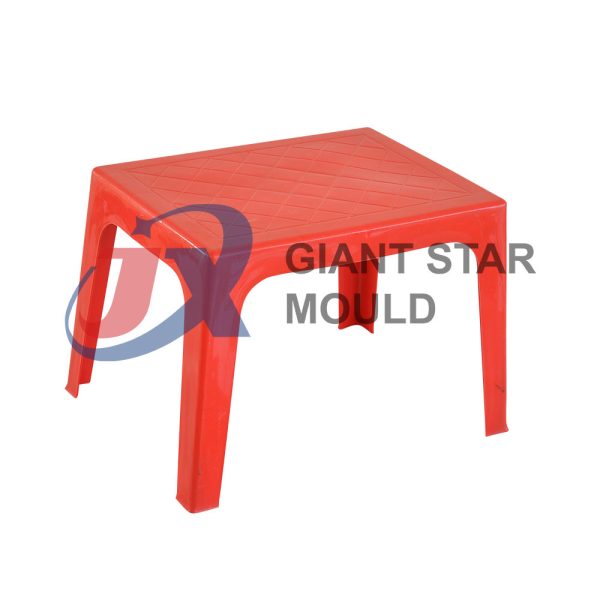
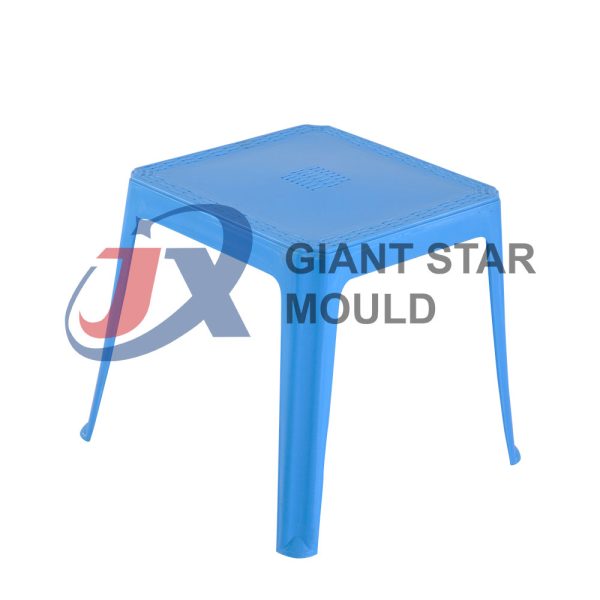
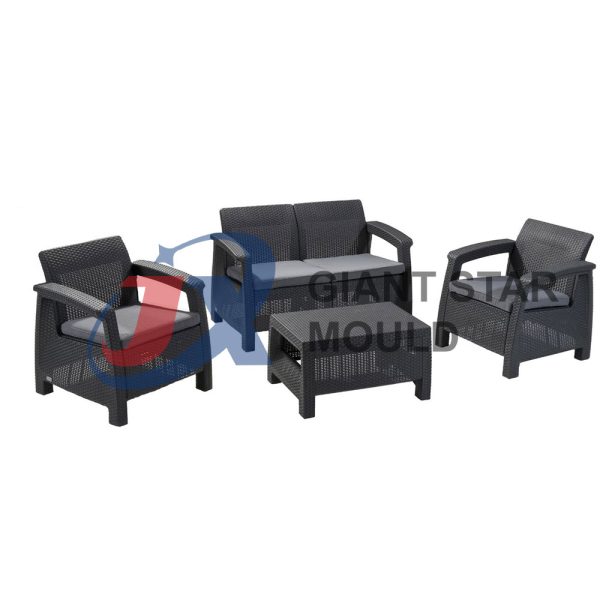
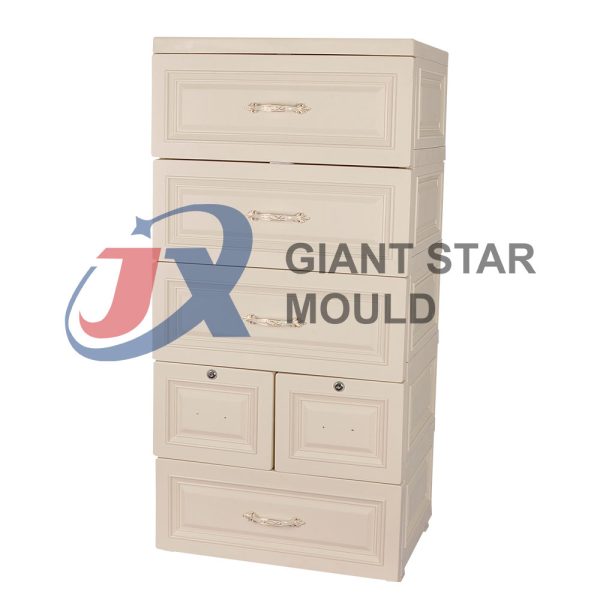
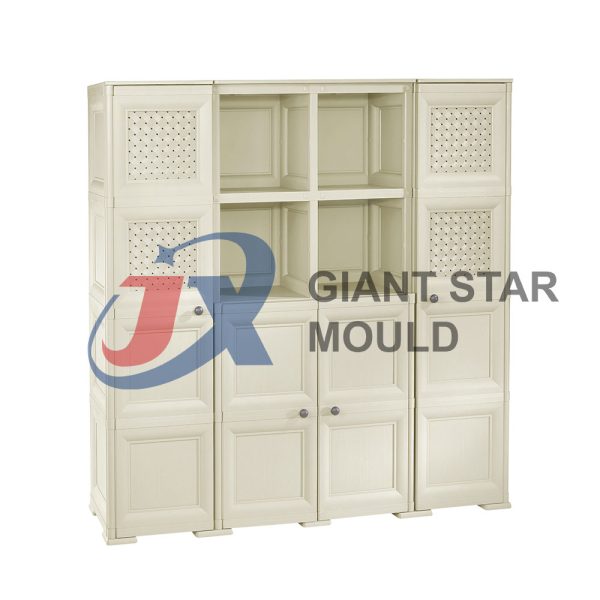
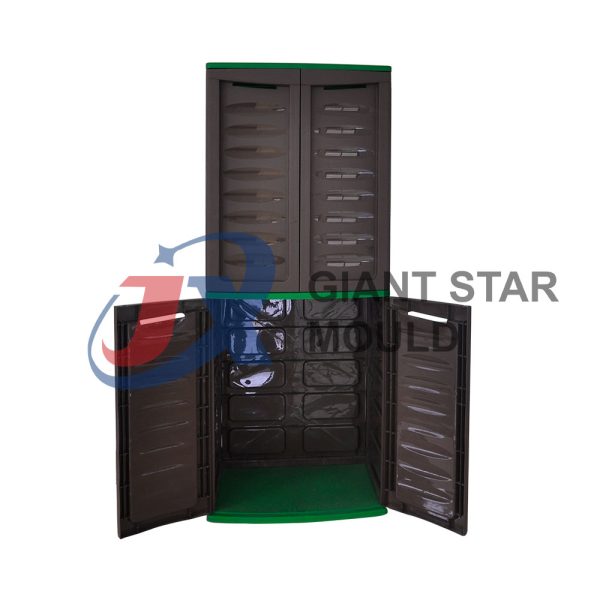
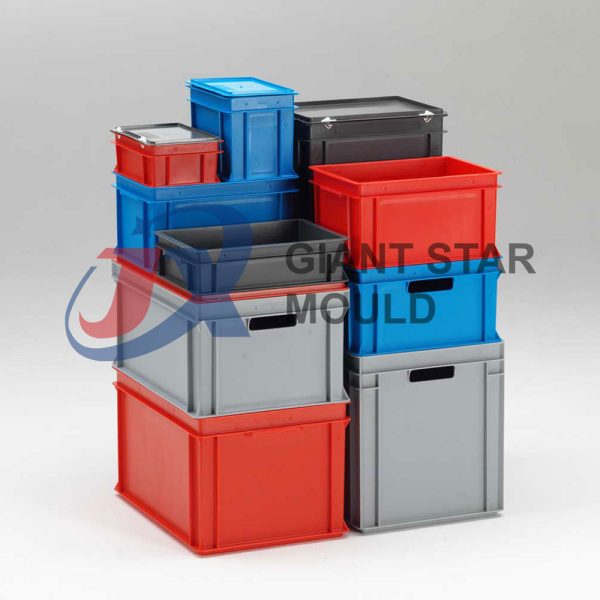
Showcase
Check out our projects!
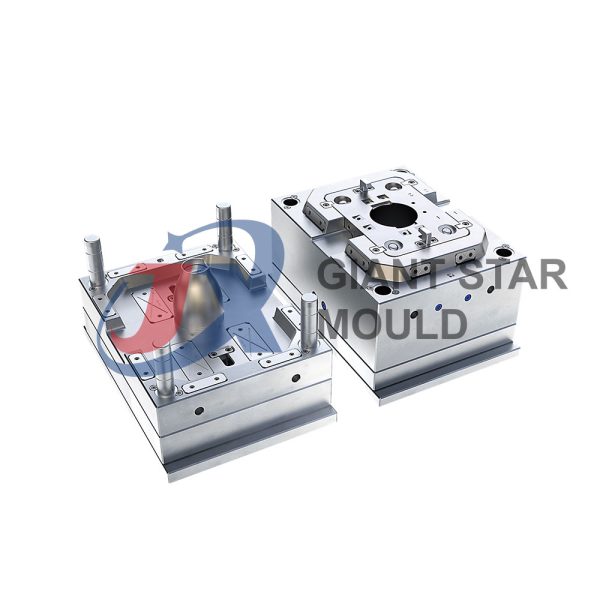
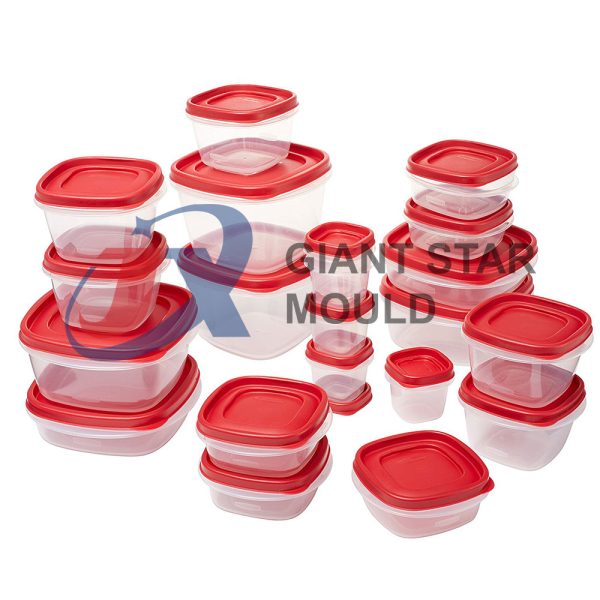
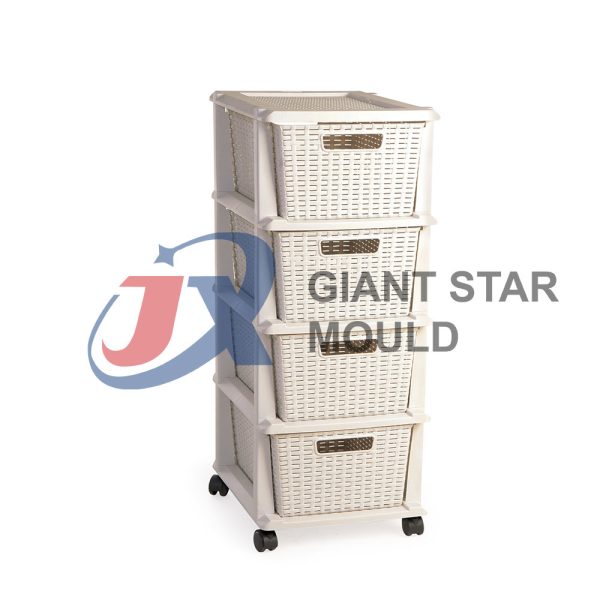
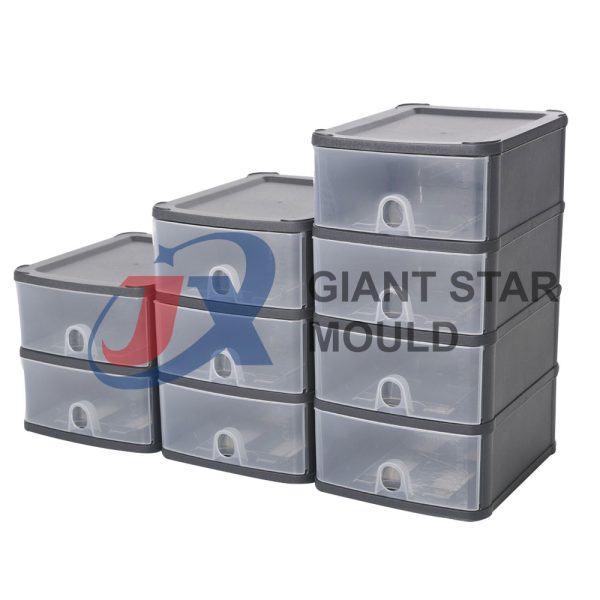
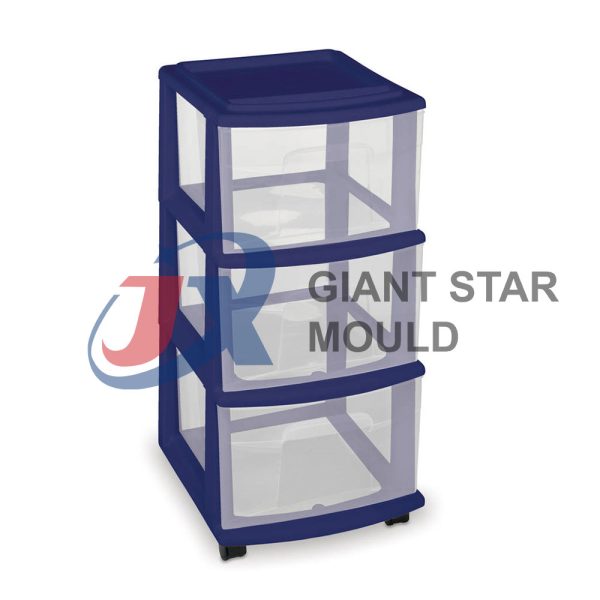
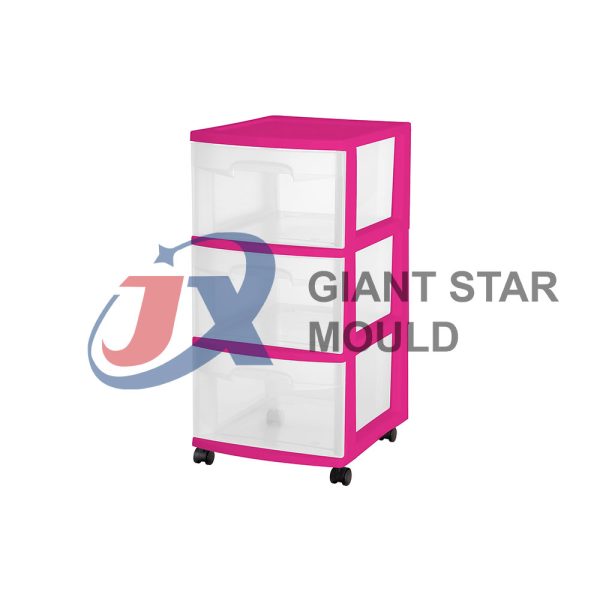
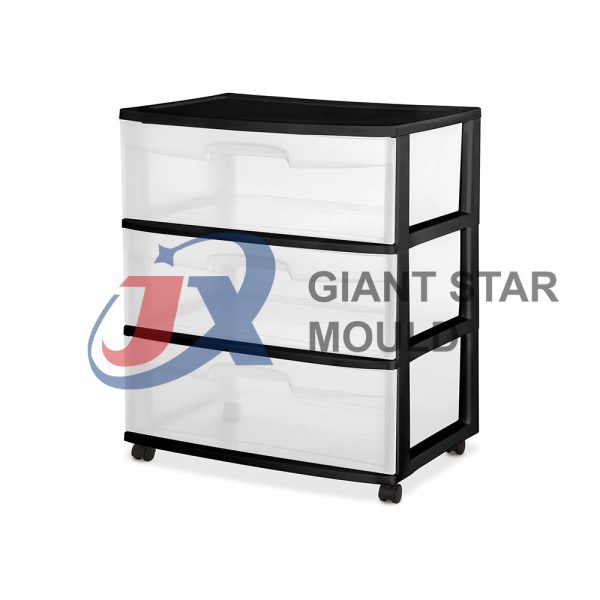
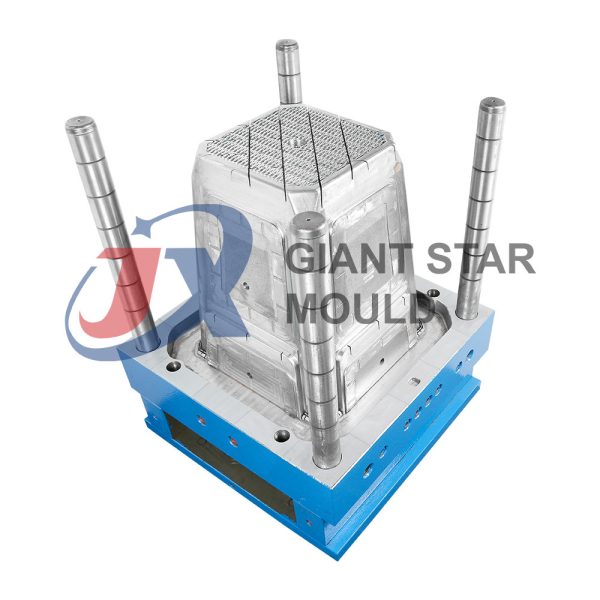
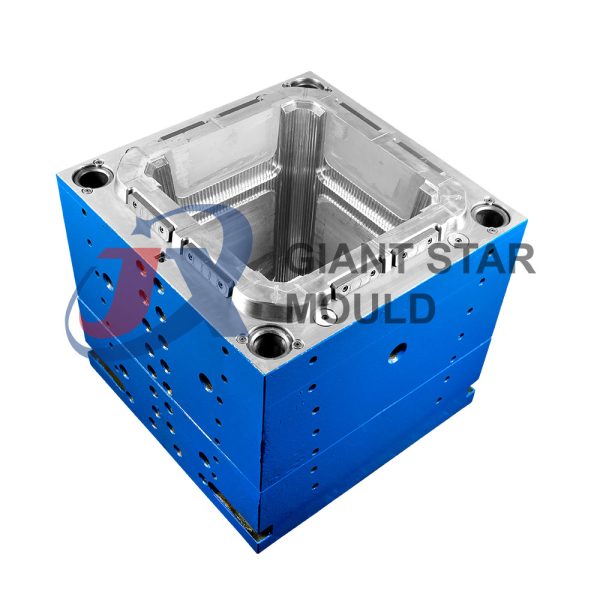
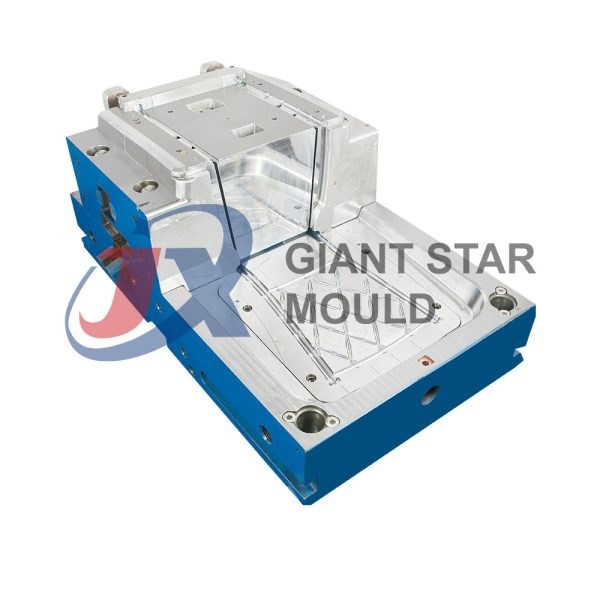
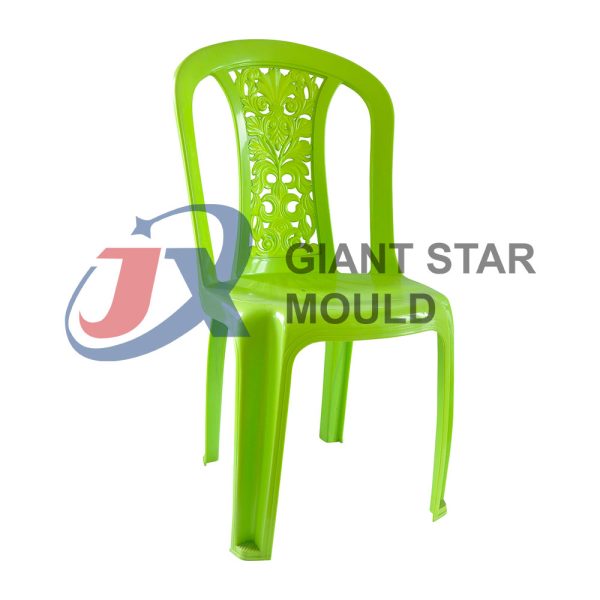
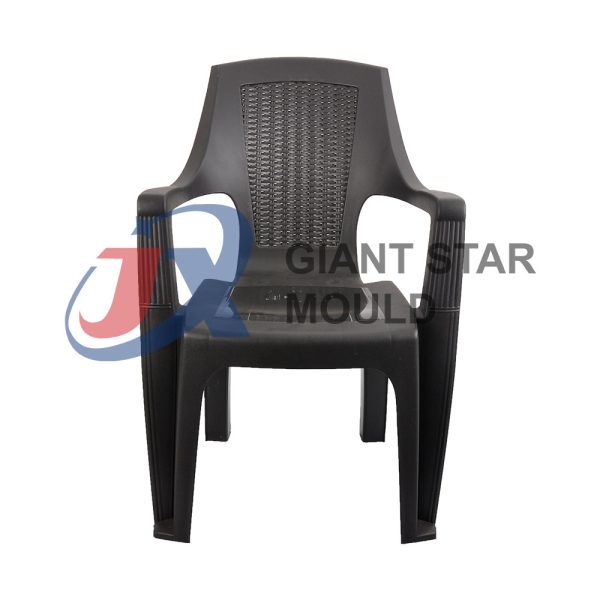
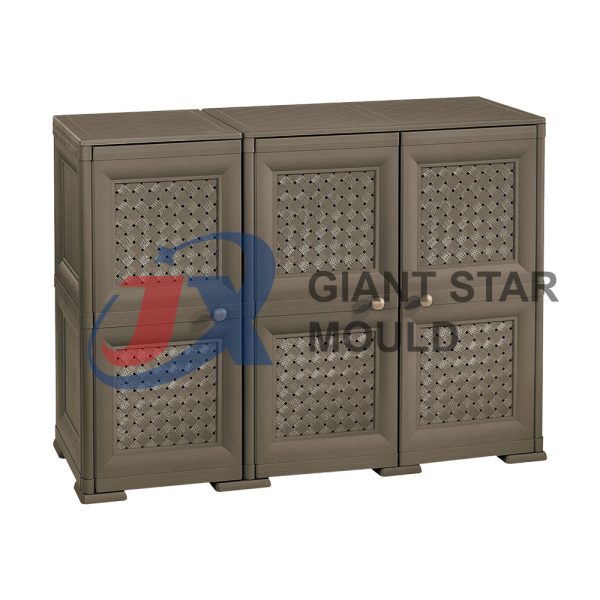
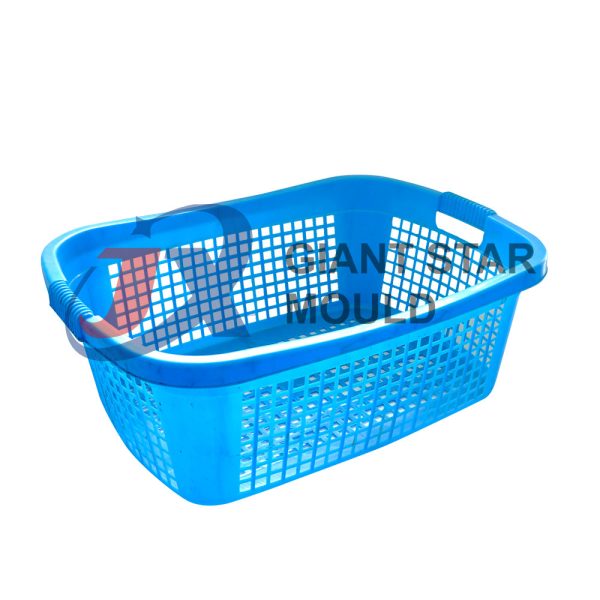
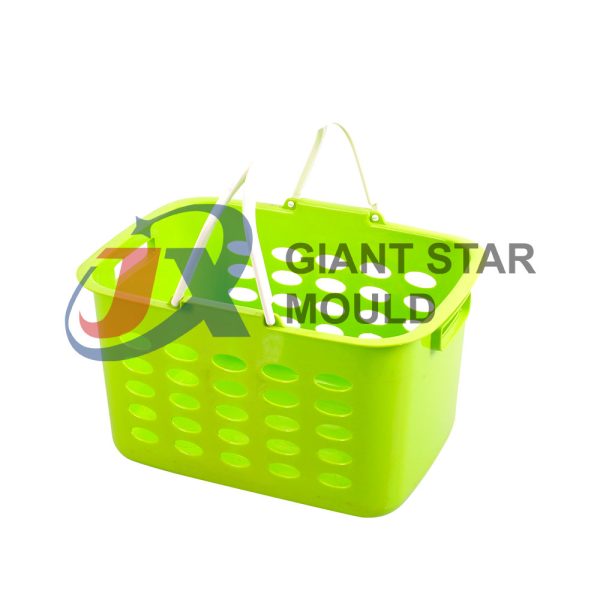
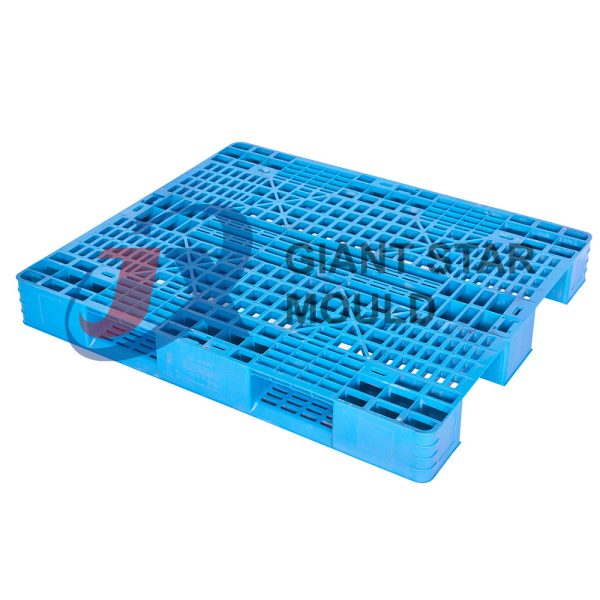
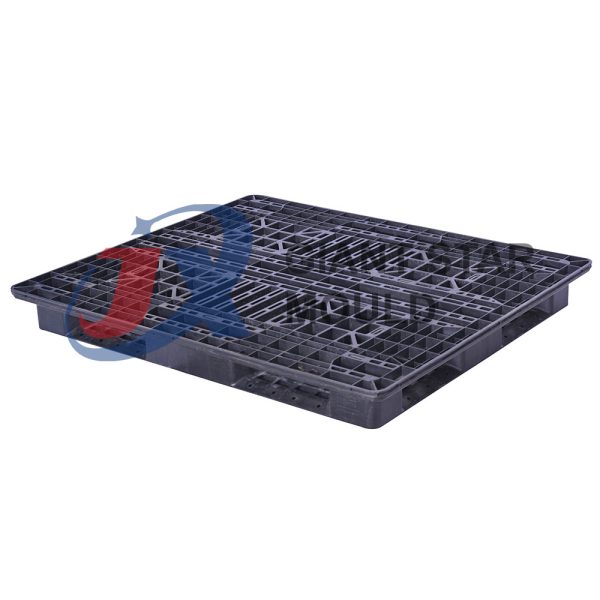
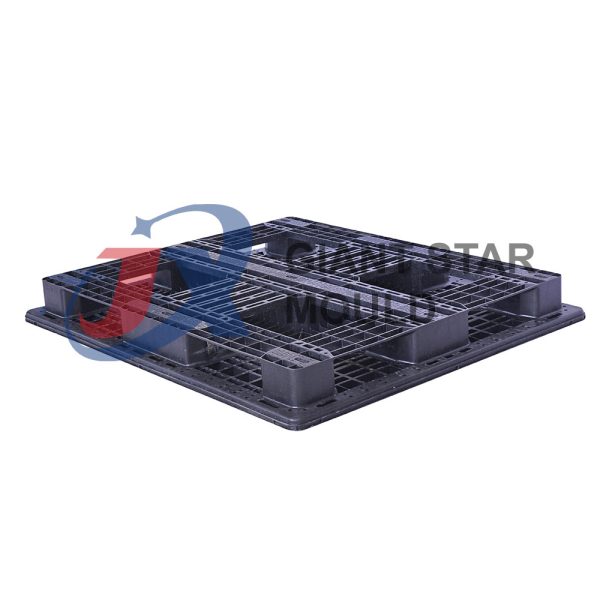
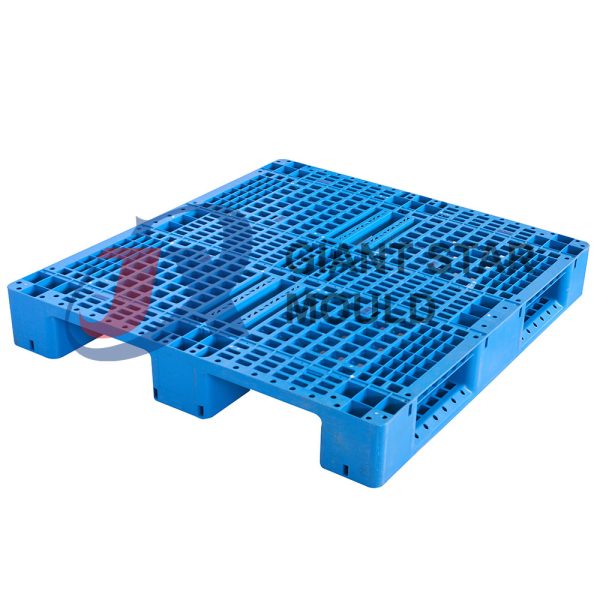
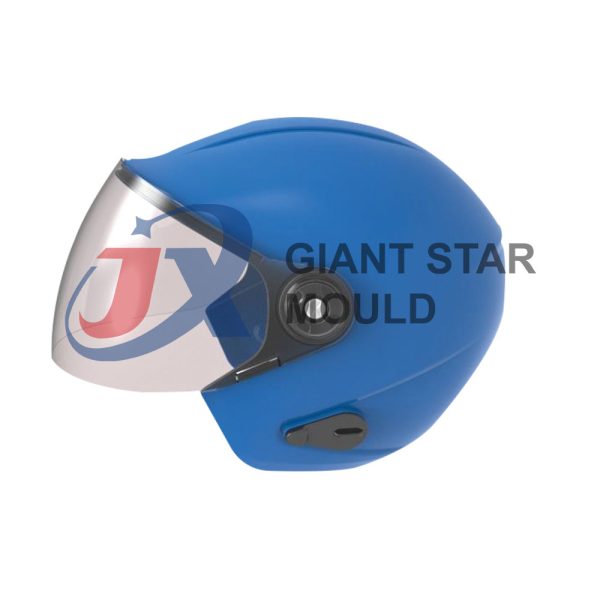
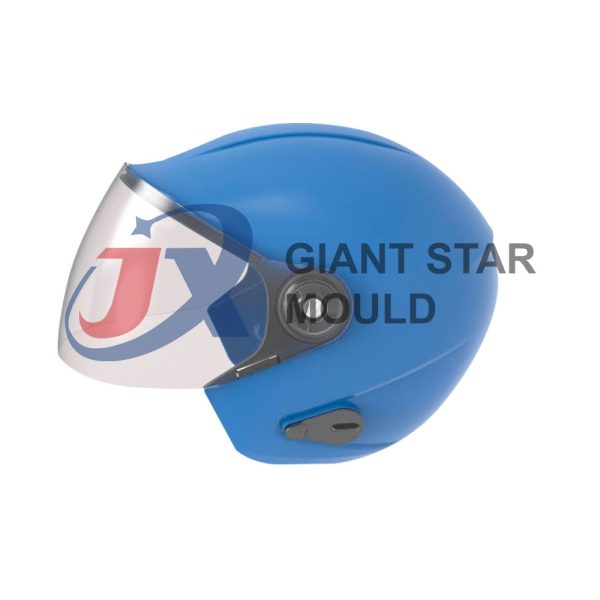
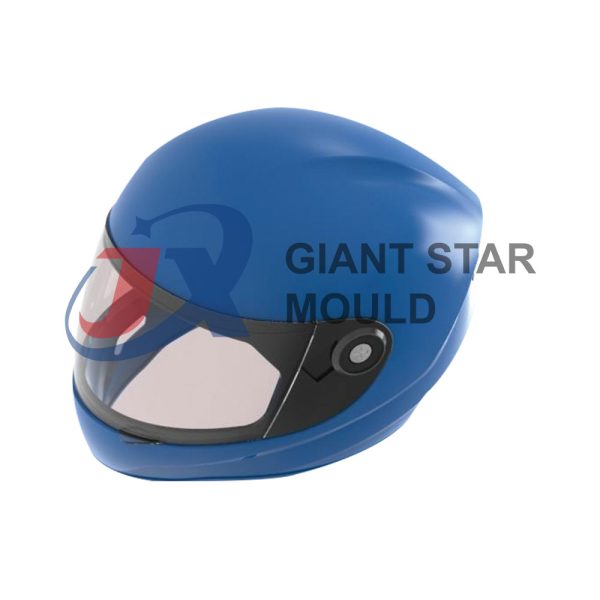
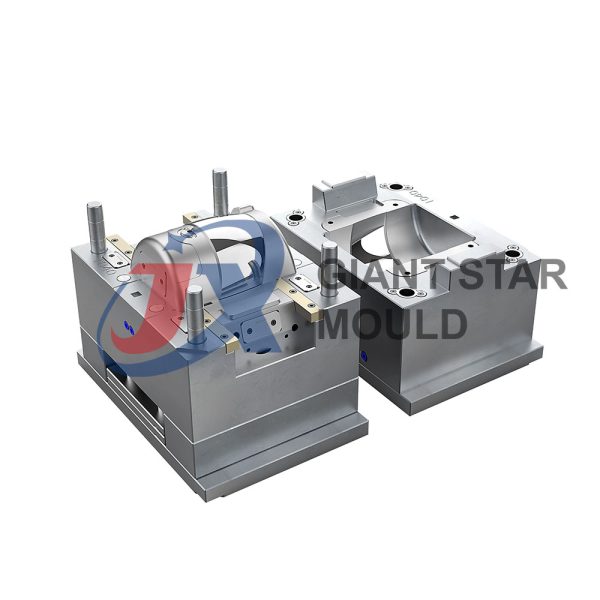
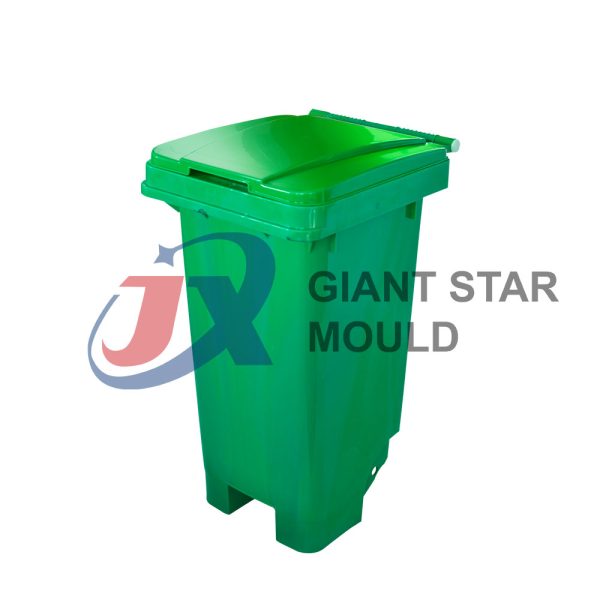
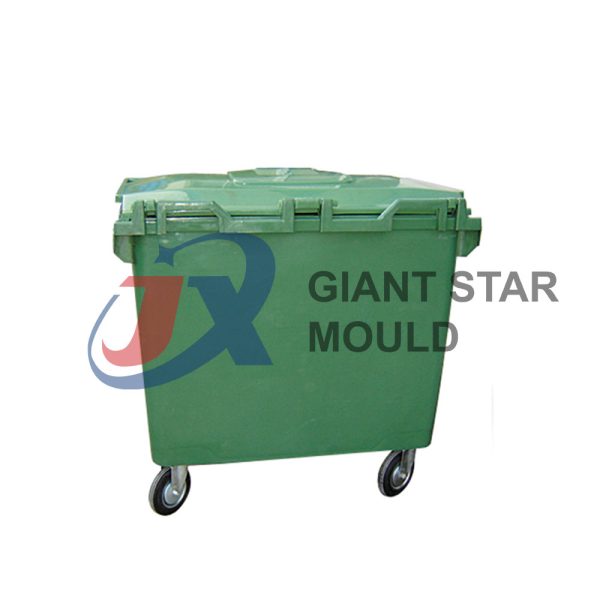
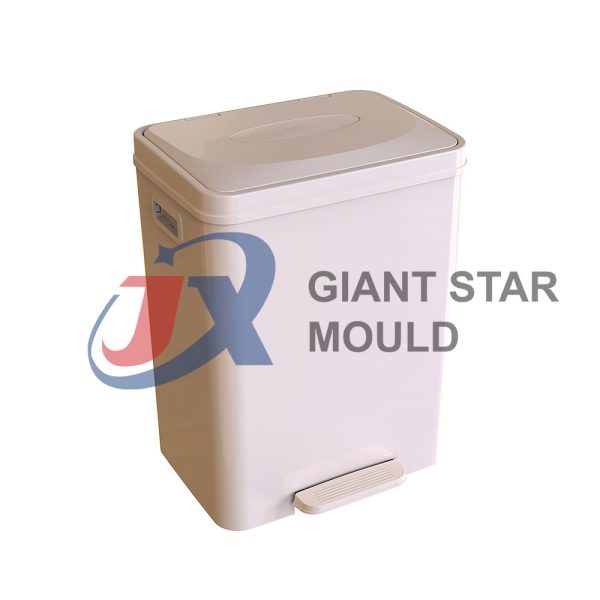
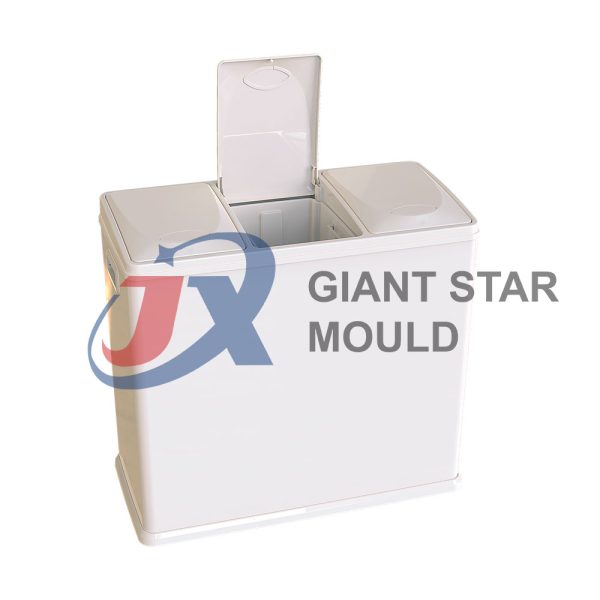
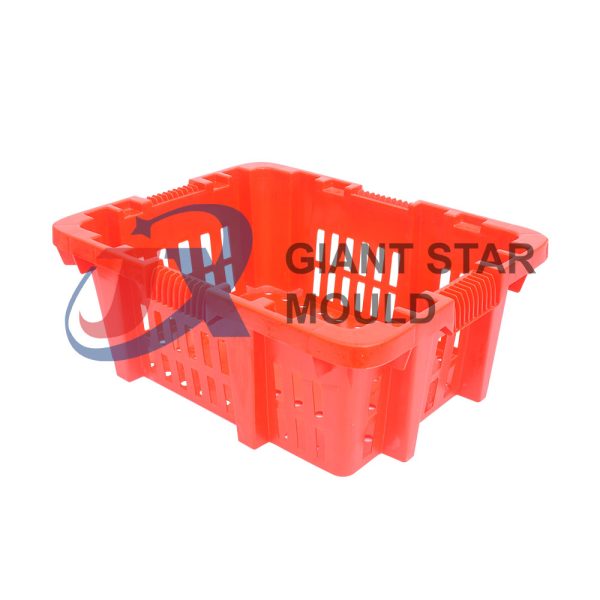
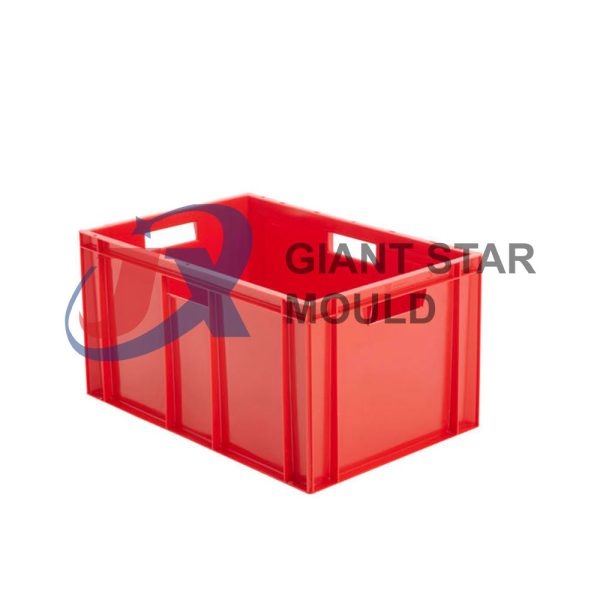
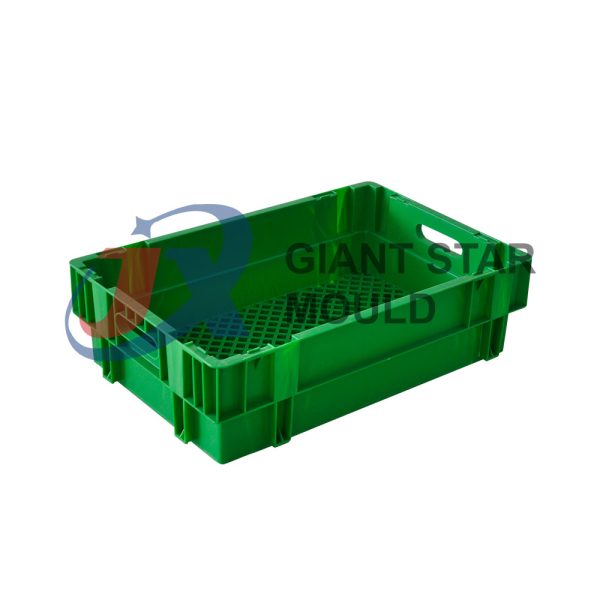
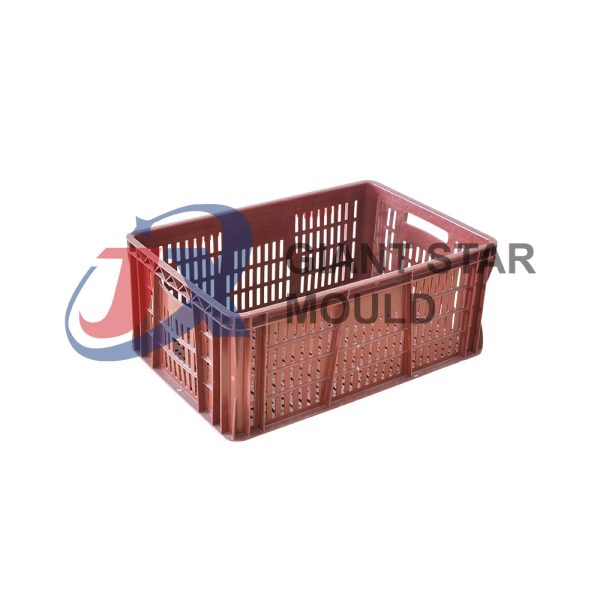
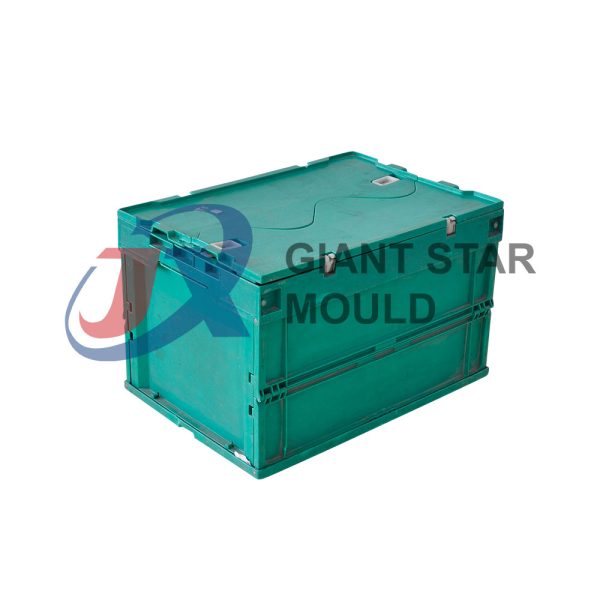
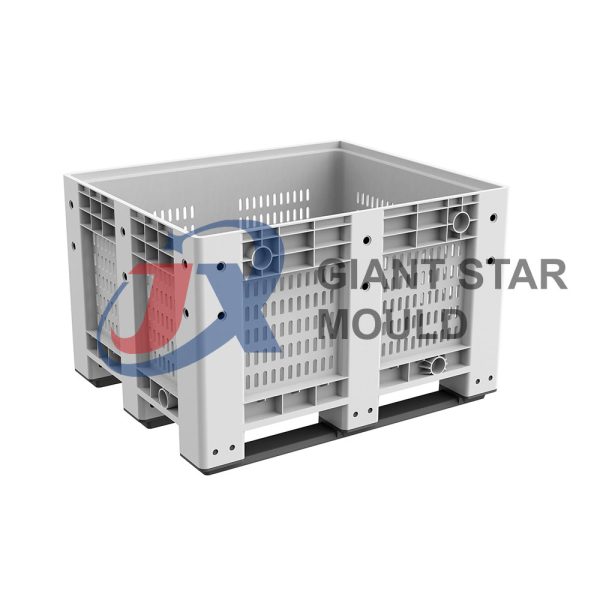
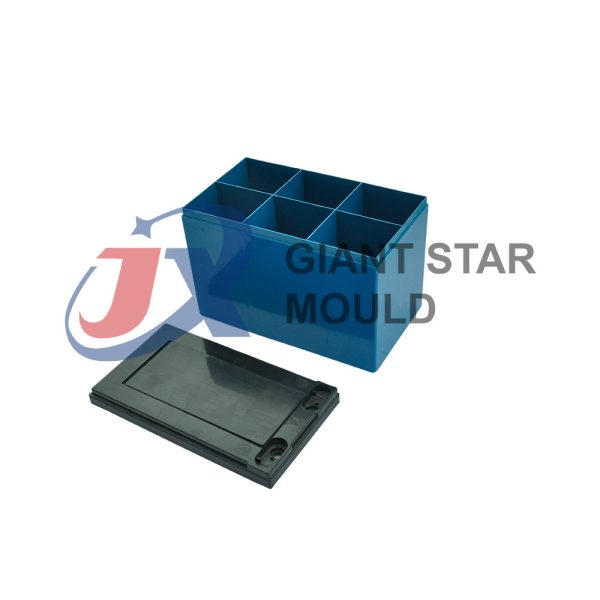
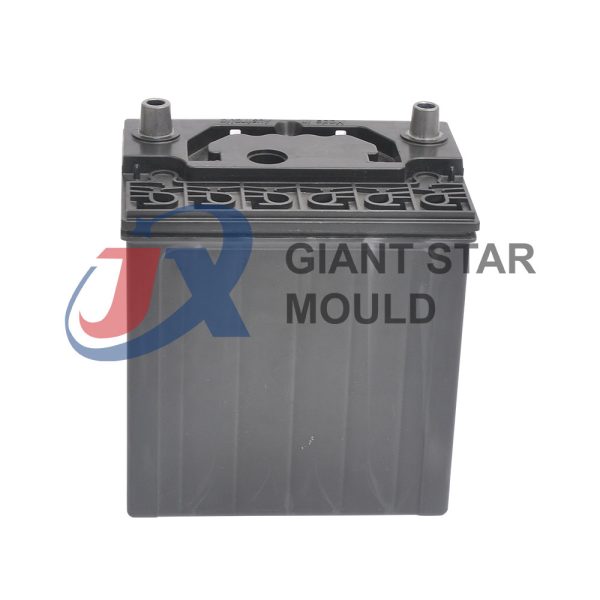
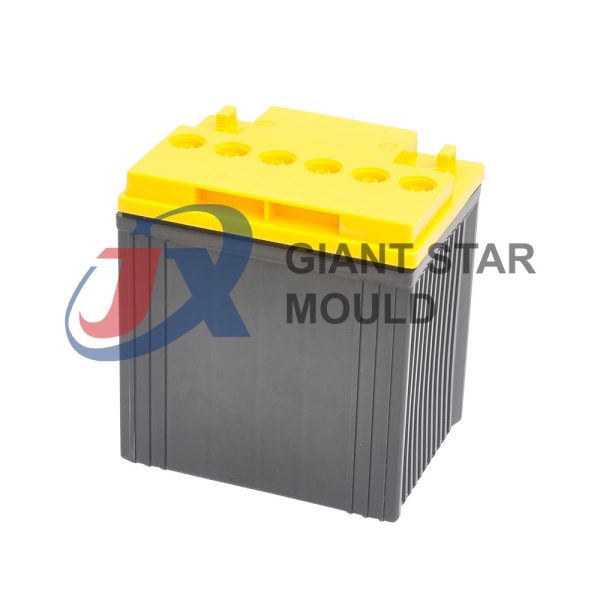
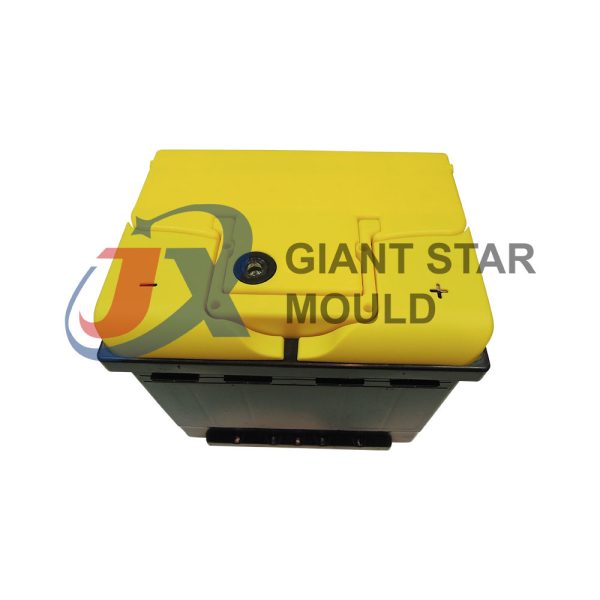
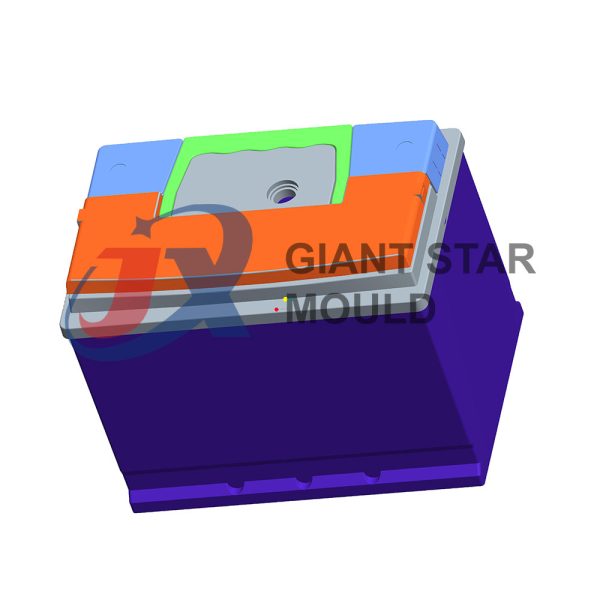
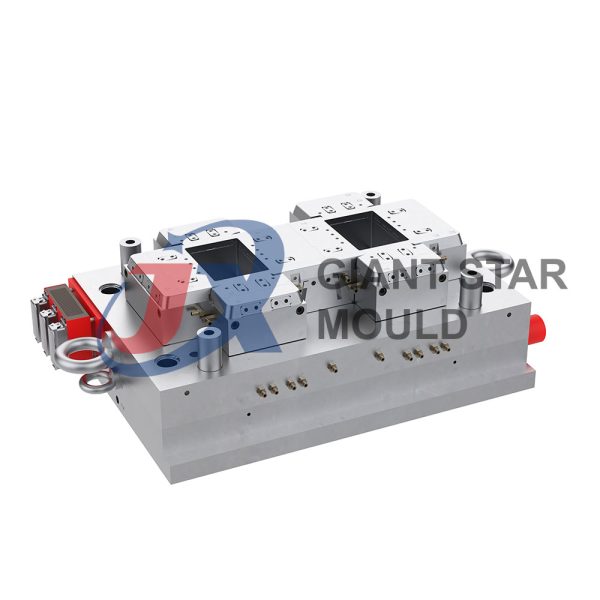
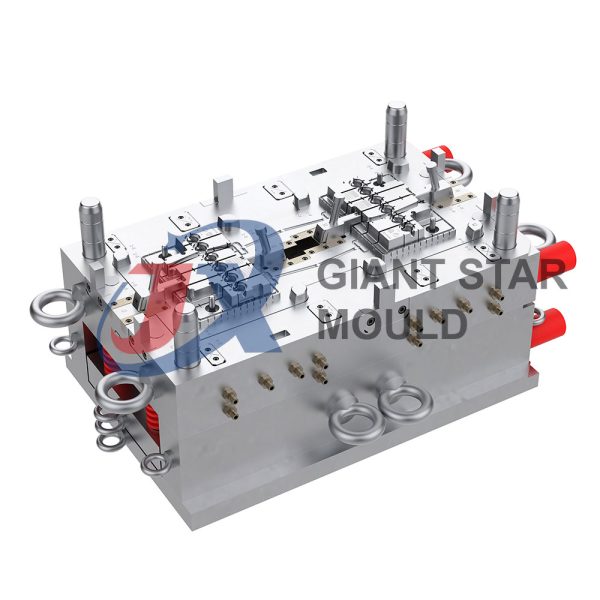
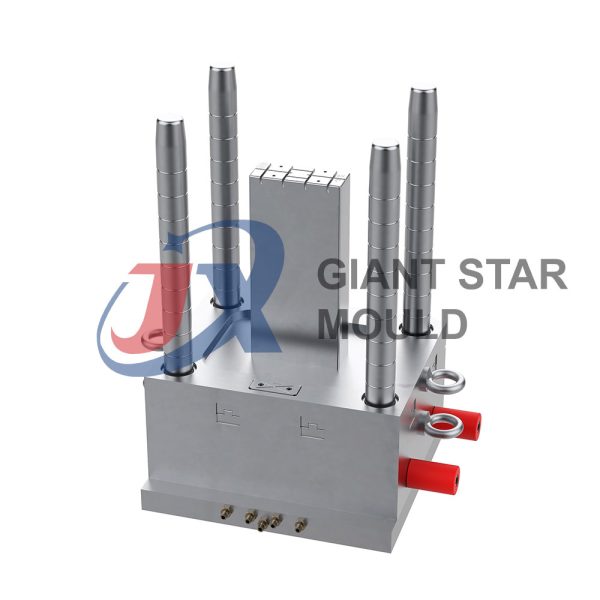
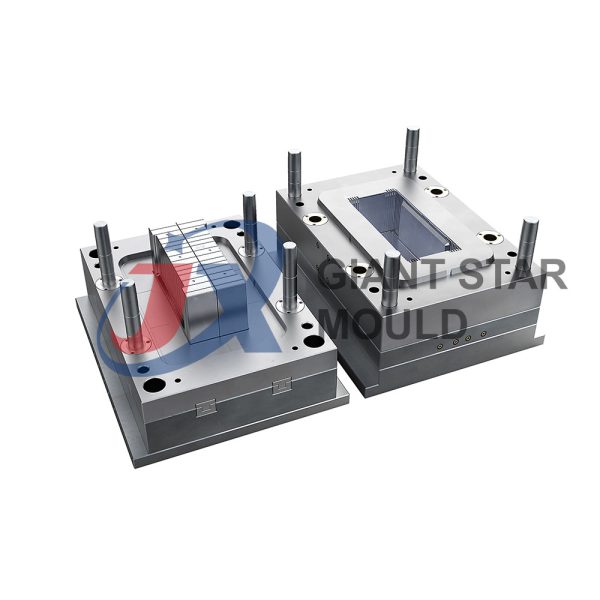
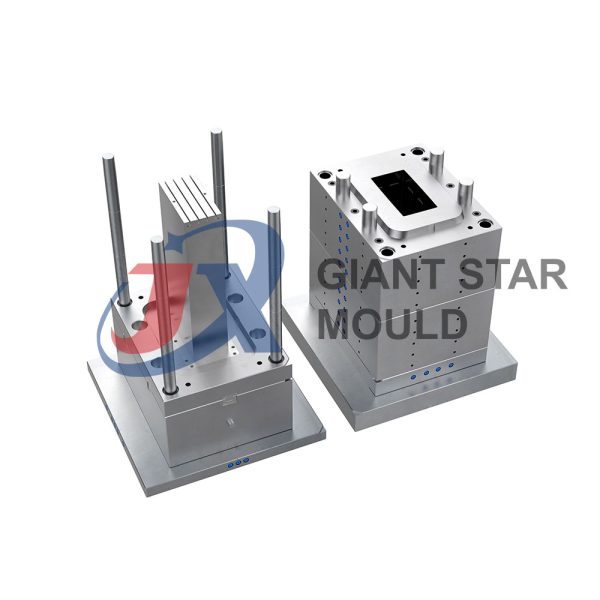
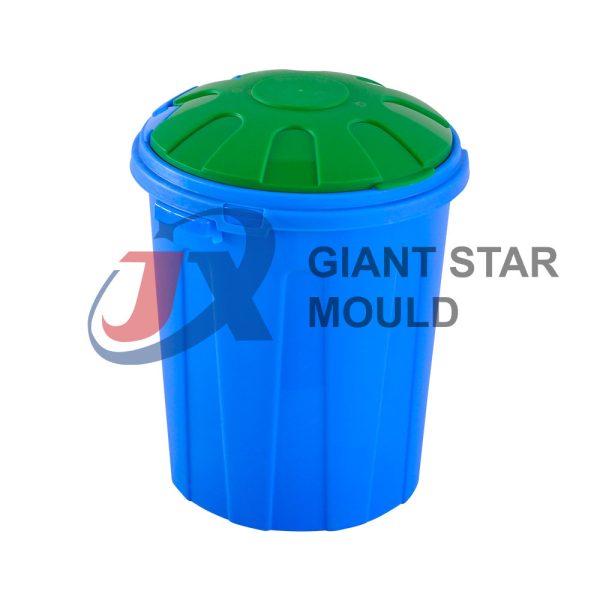
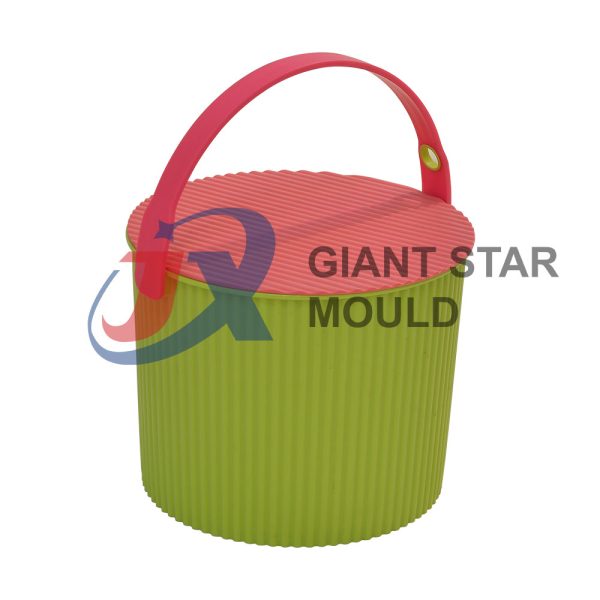
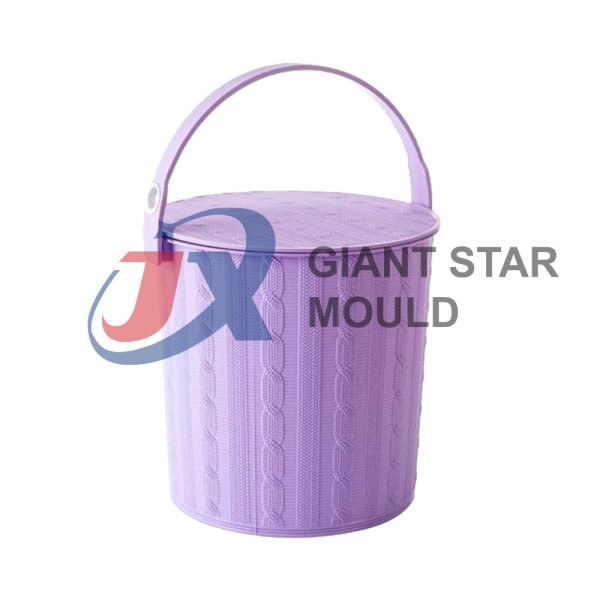
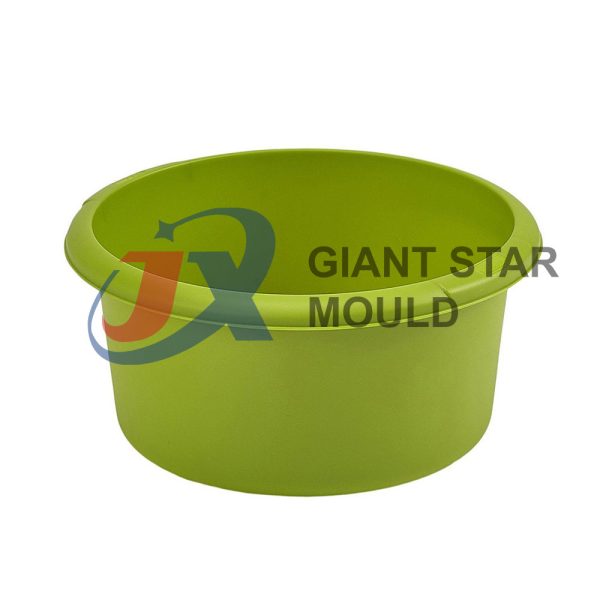
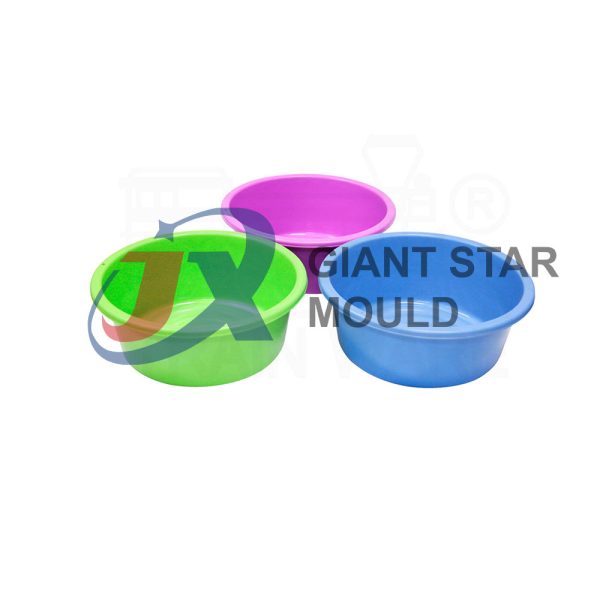
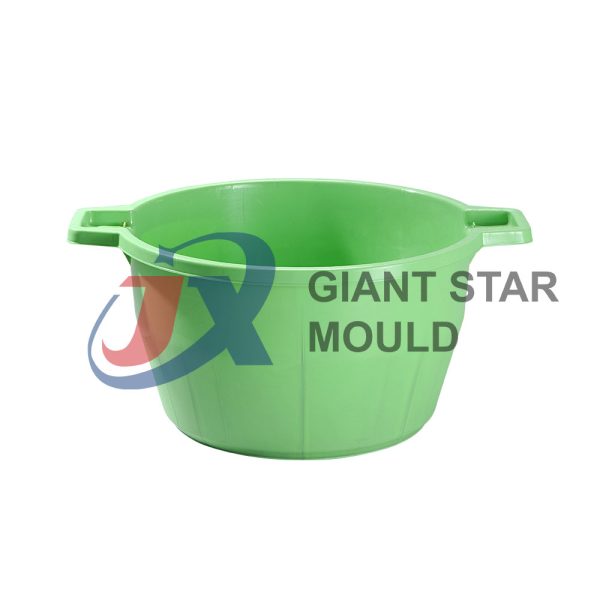
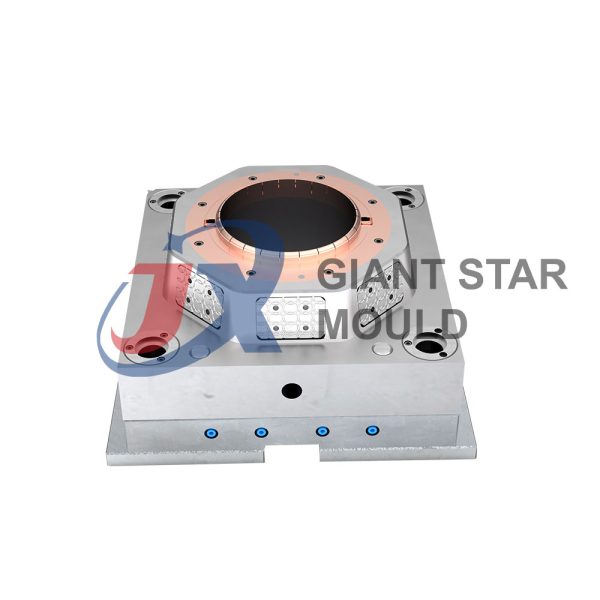
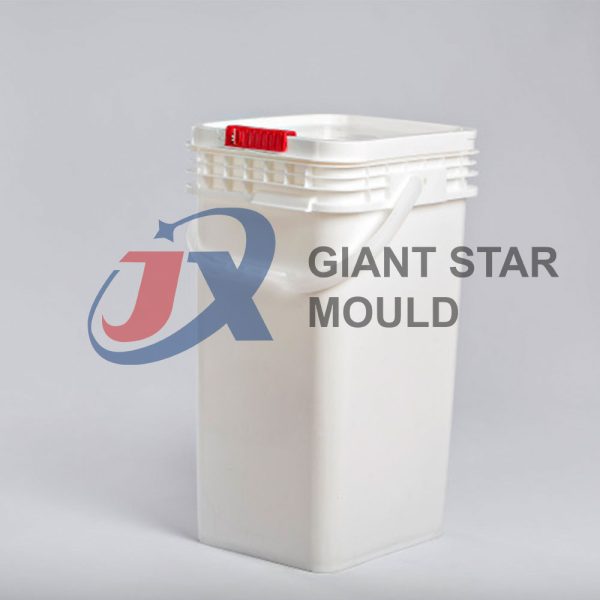
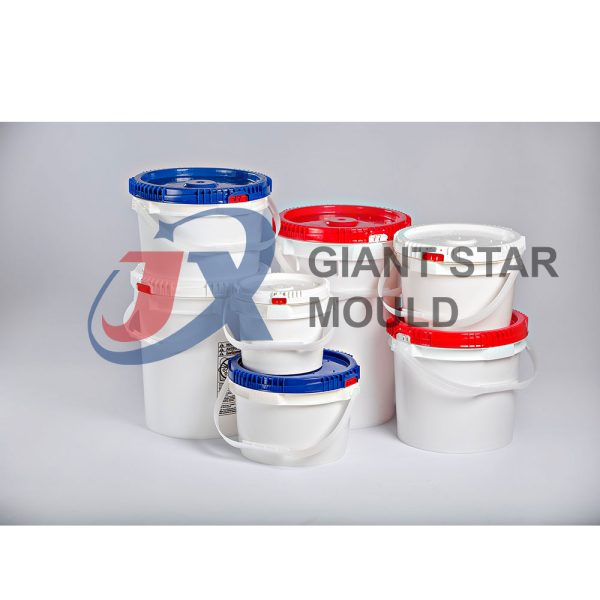
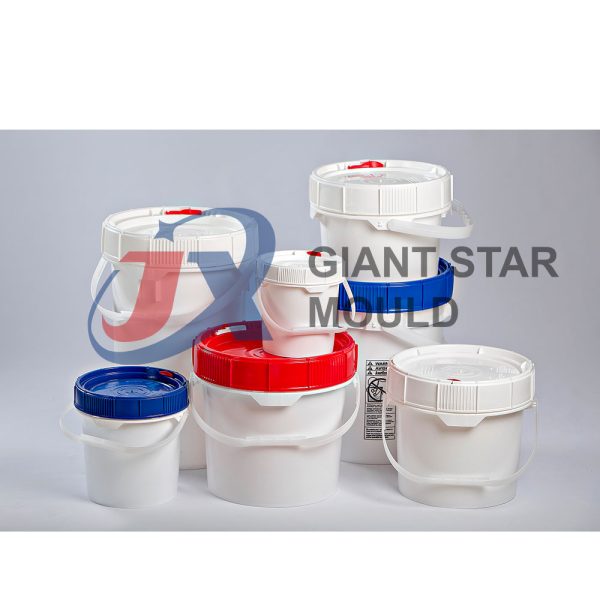
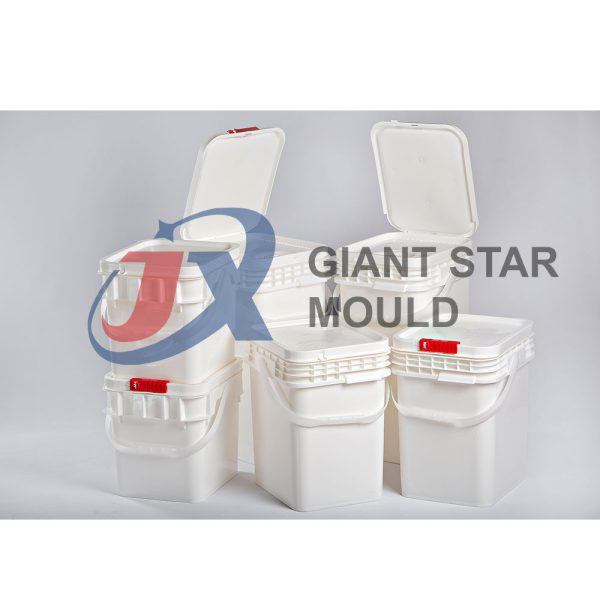
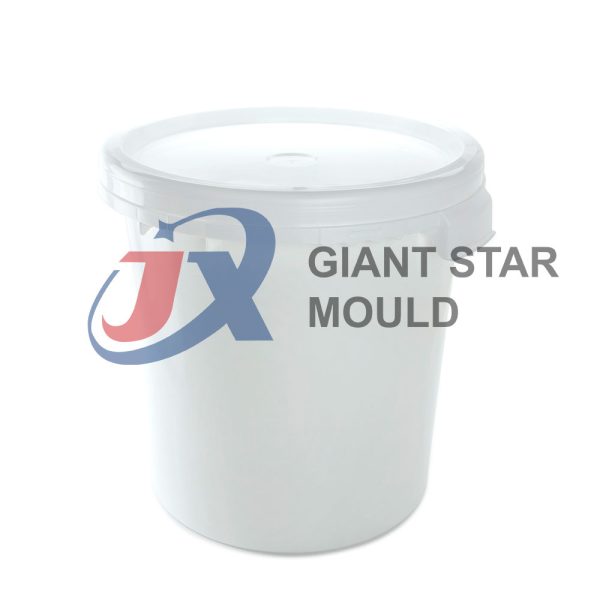
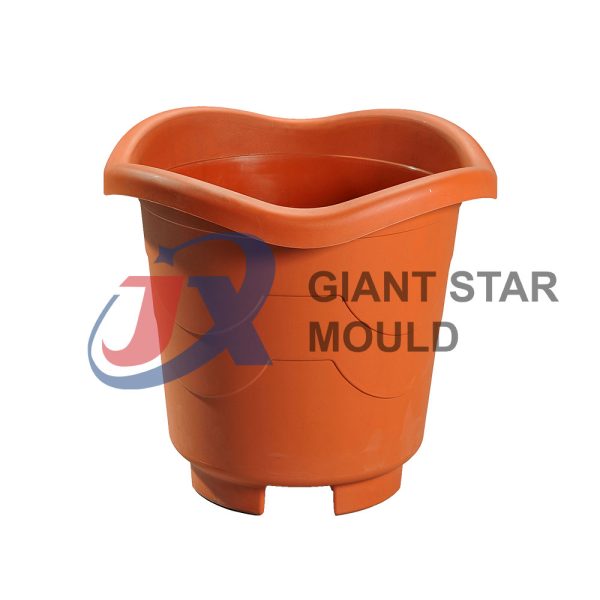
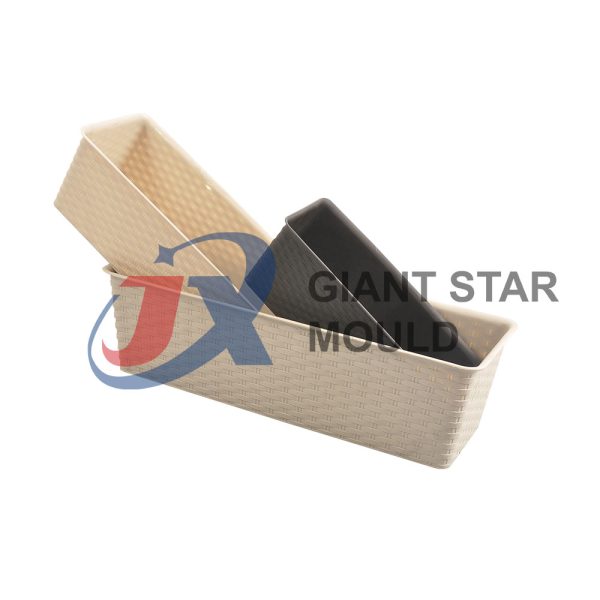
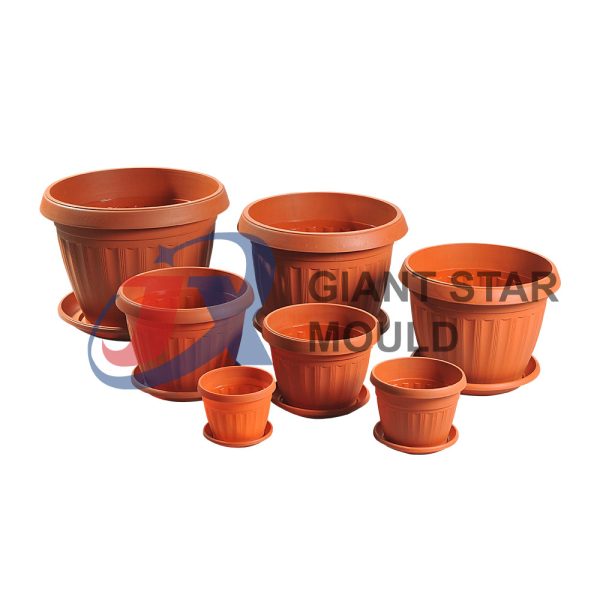
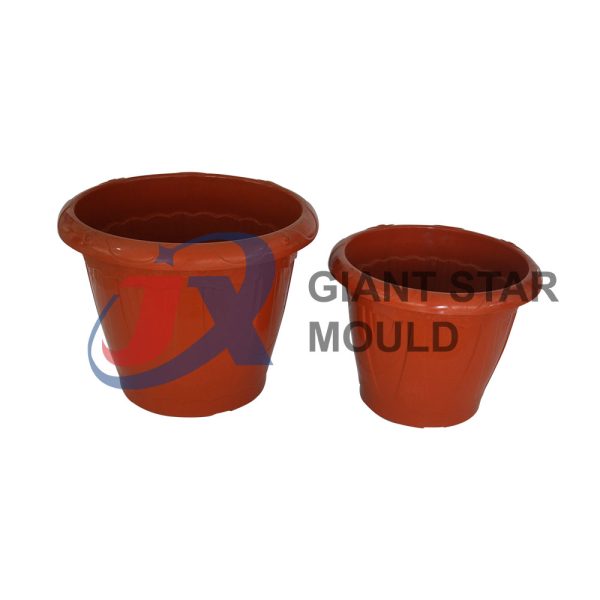
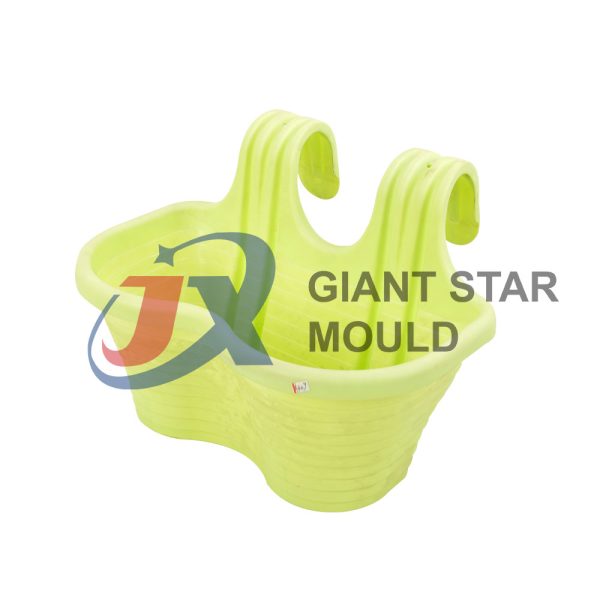
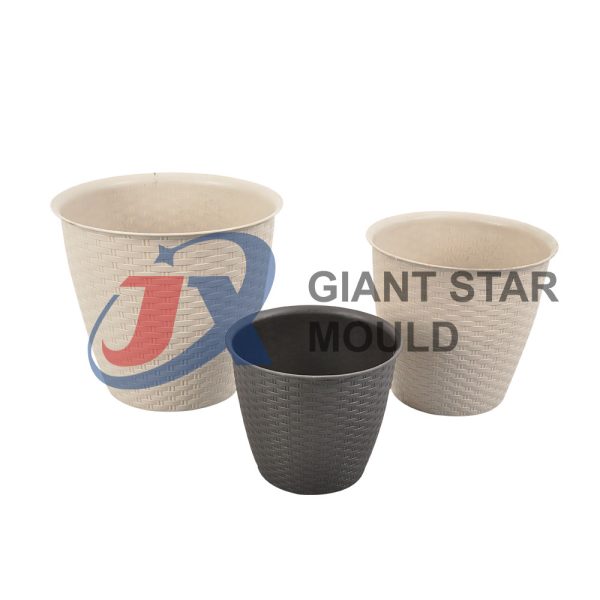
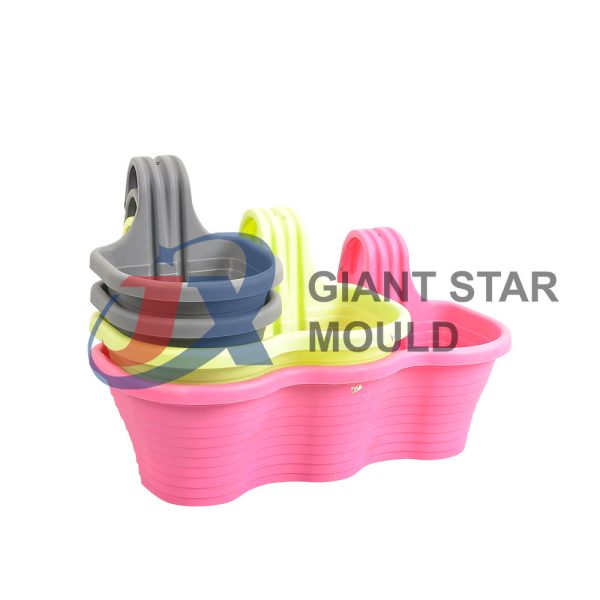
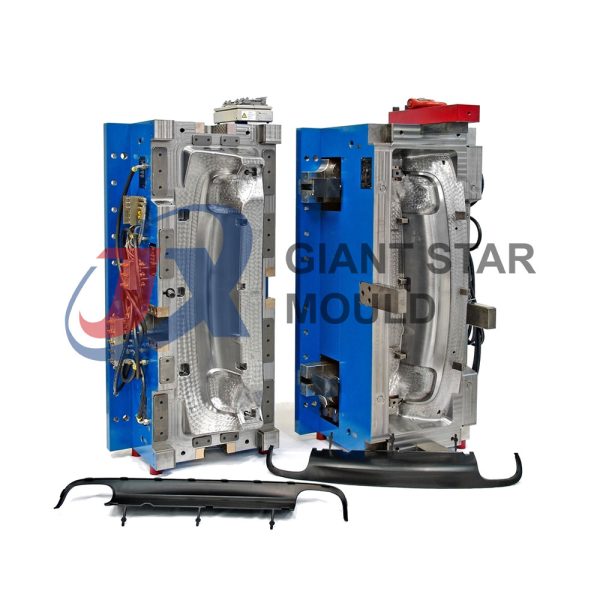
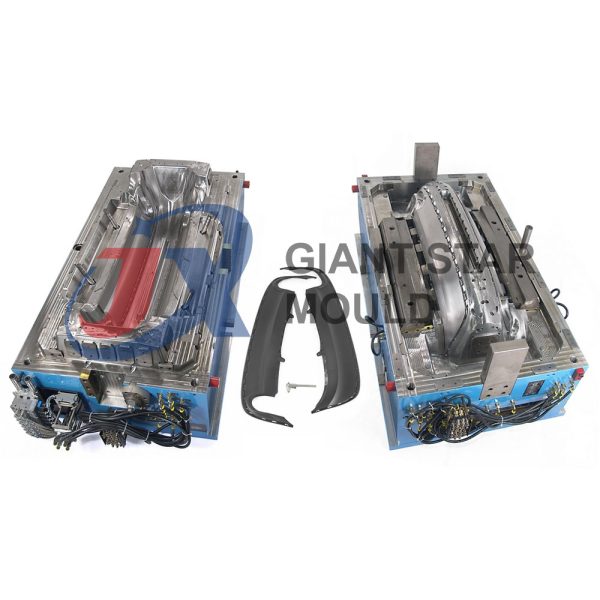
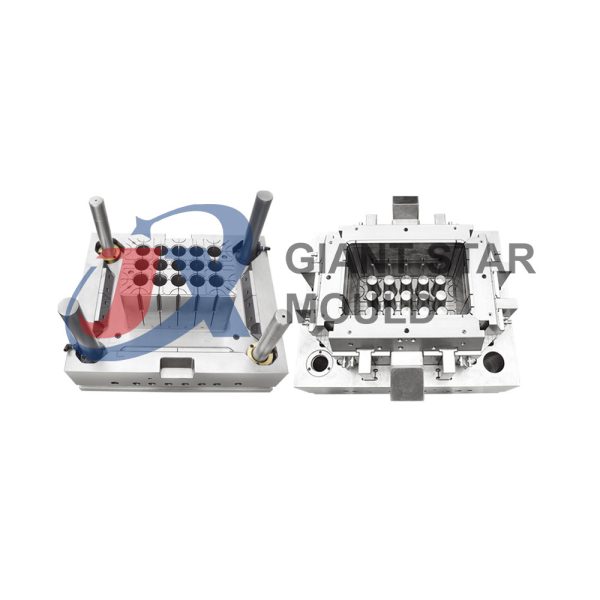
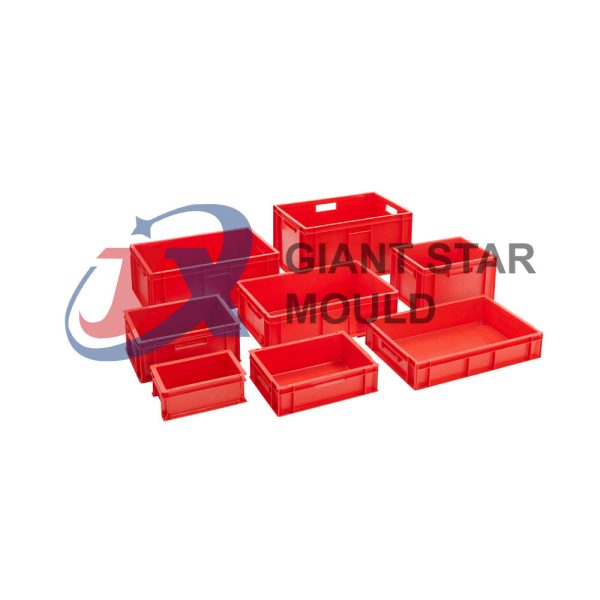
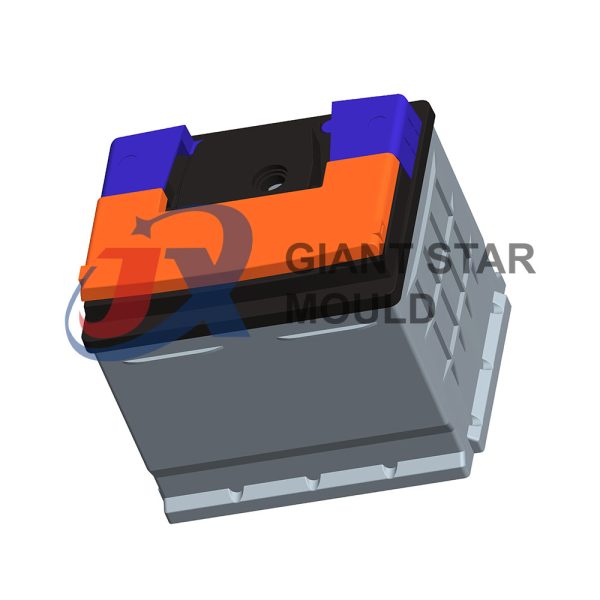
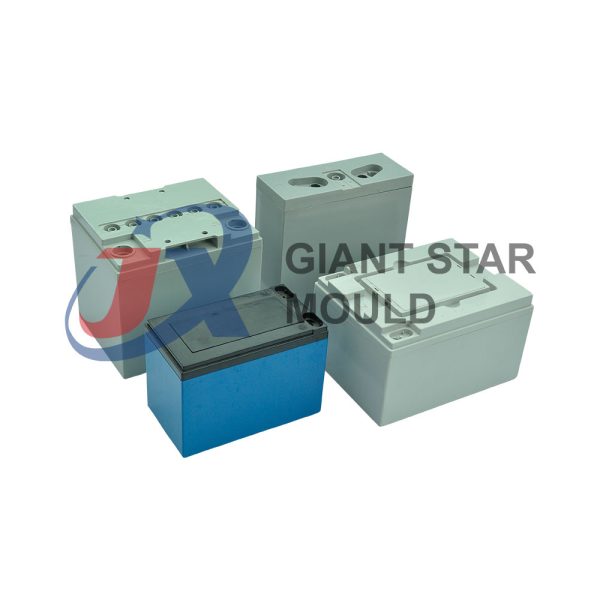
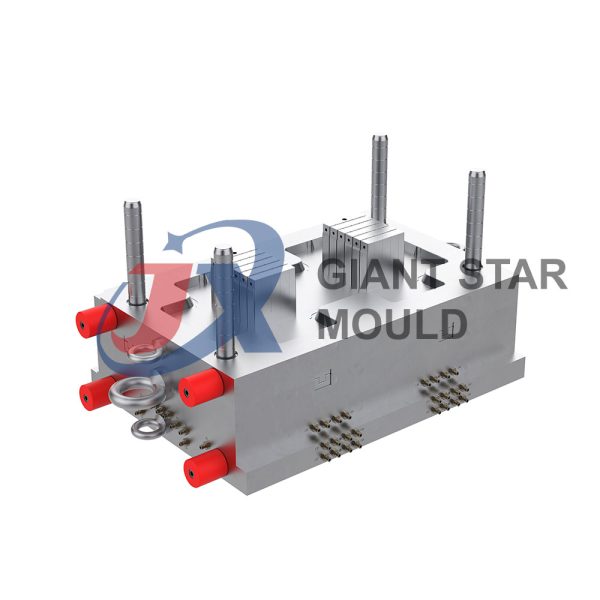
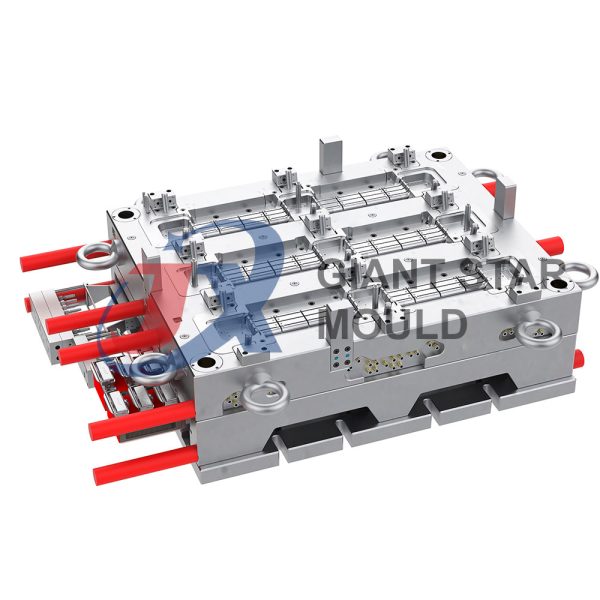
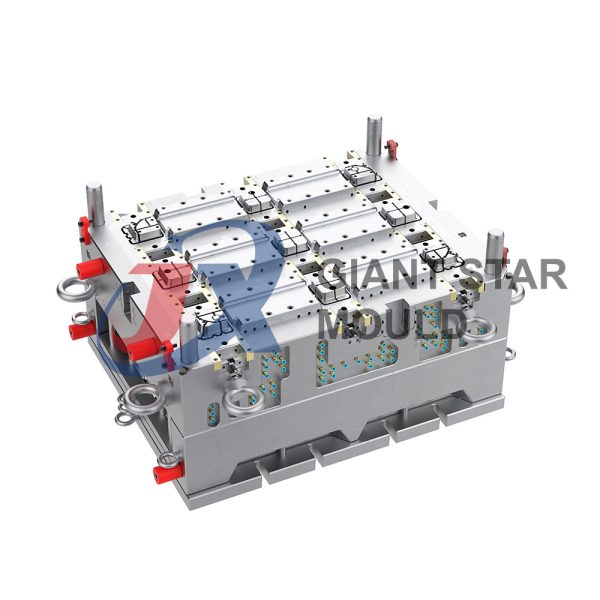
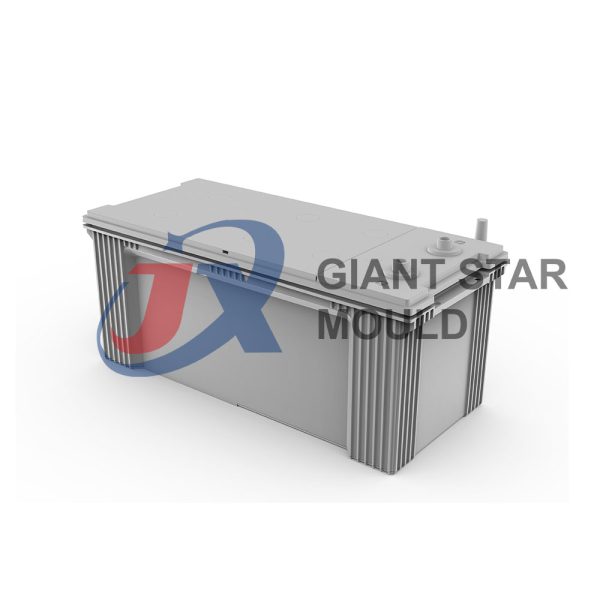
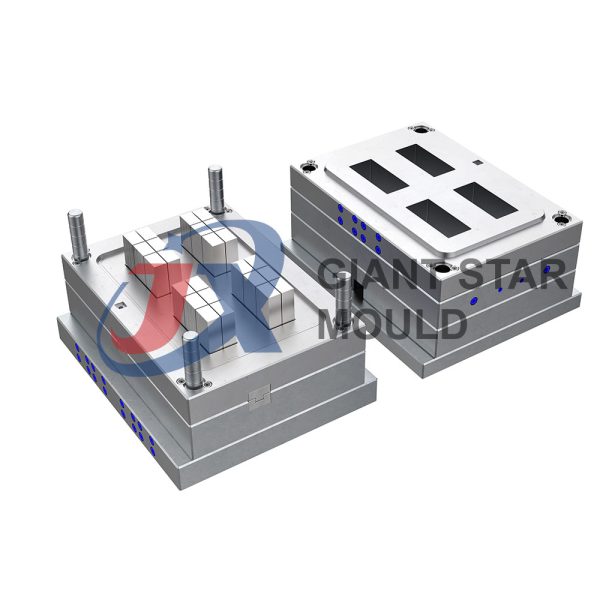
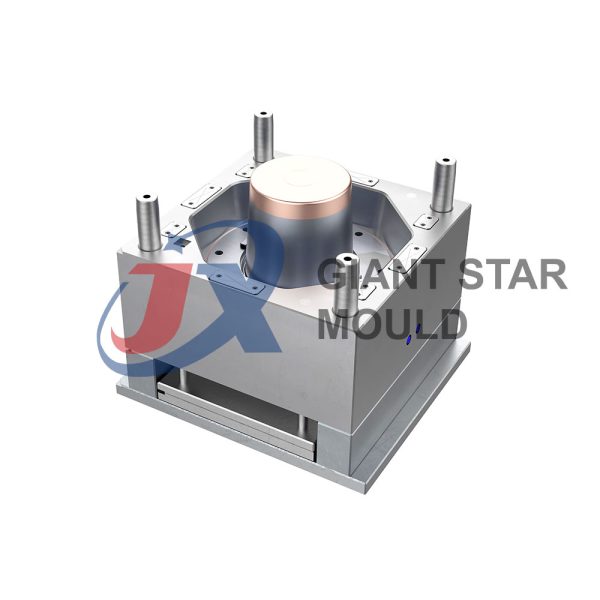
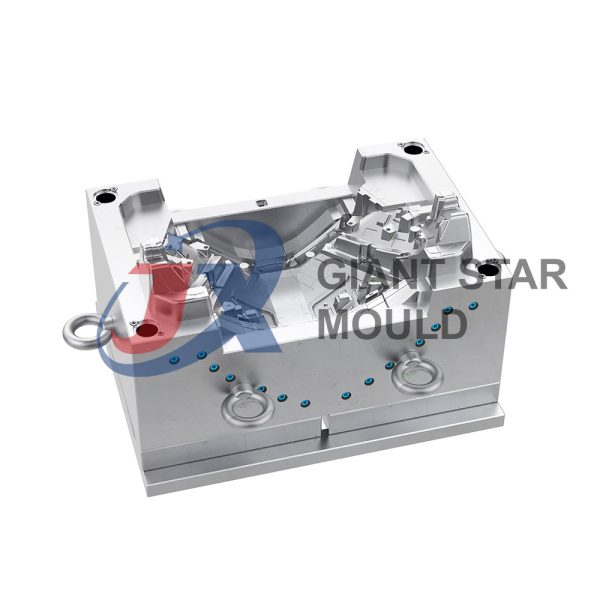
Battery Container Mould 32
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
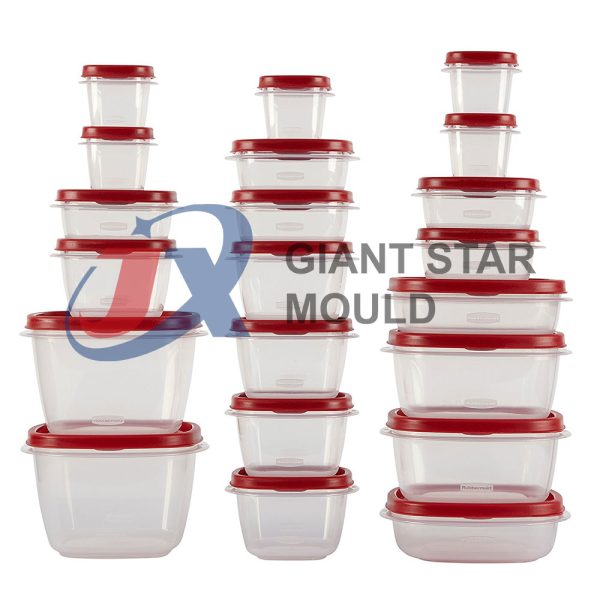
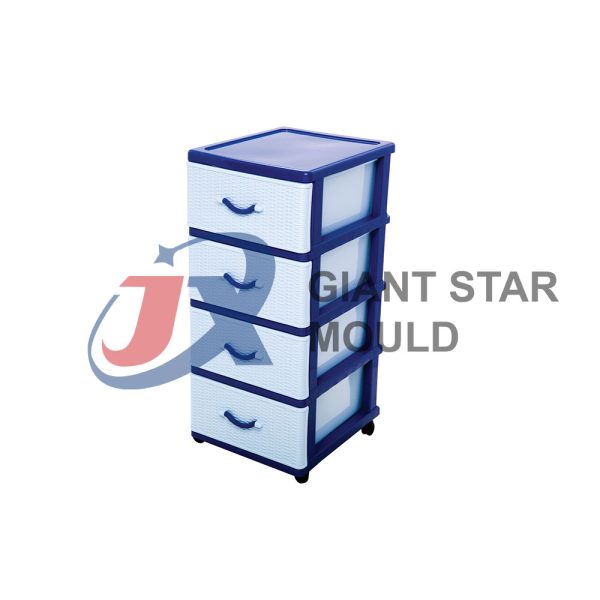
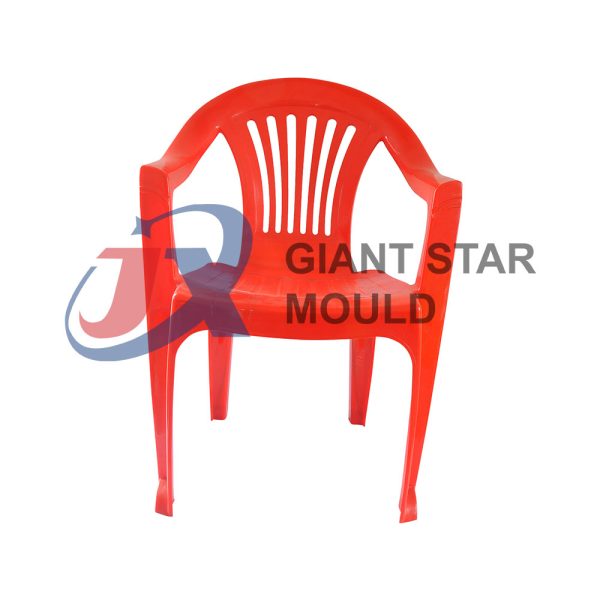
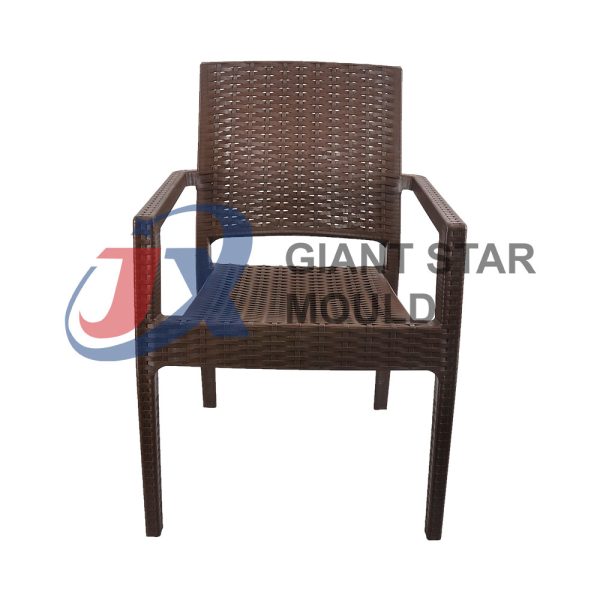
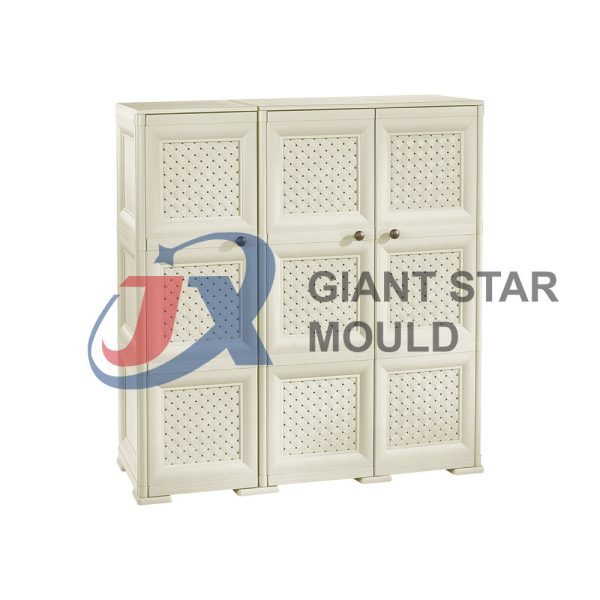
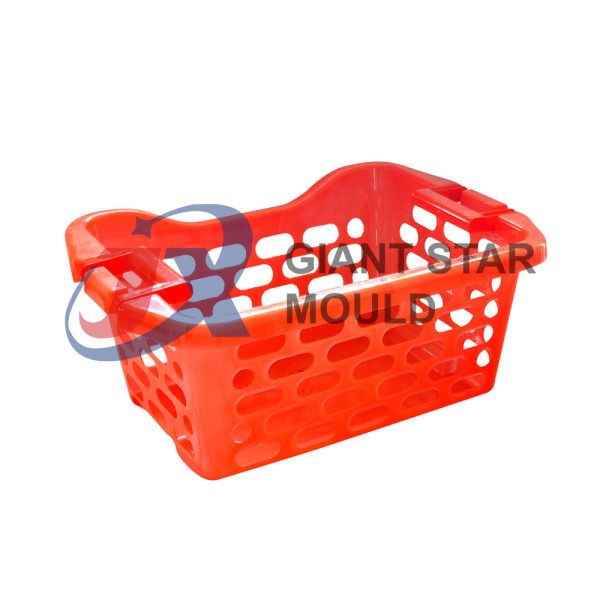
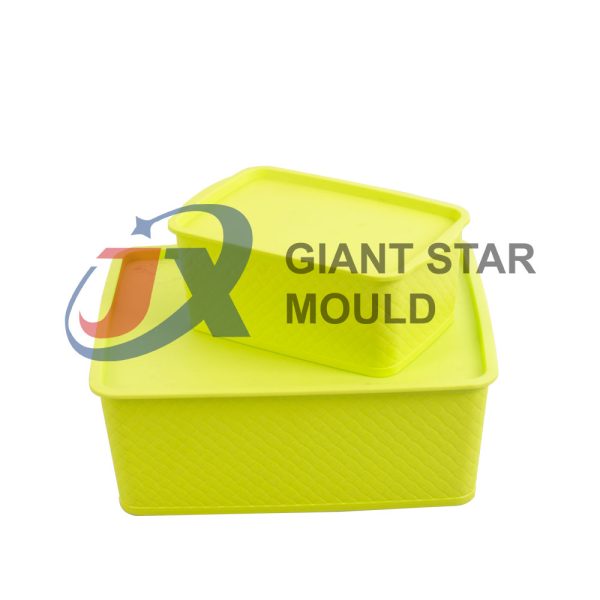
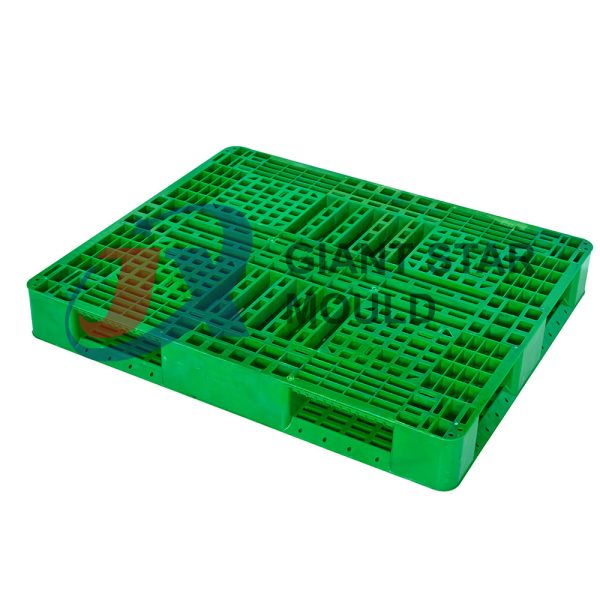
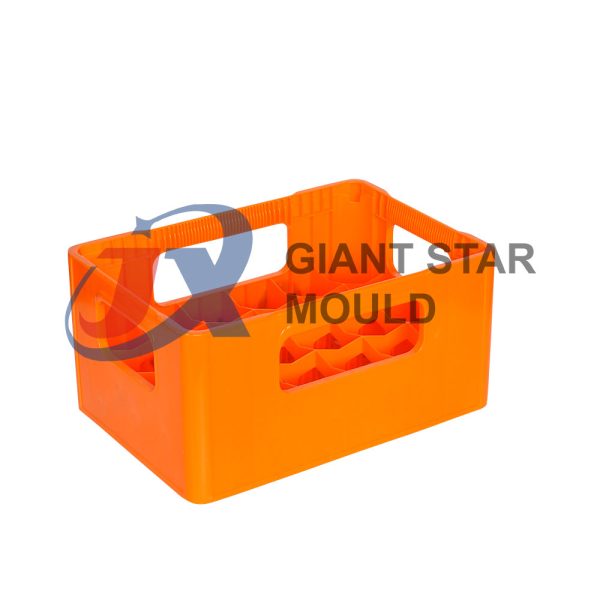
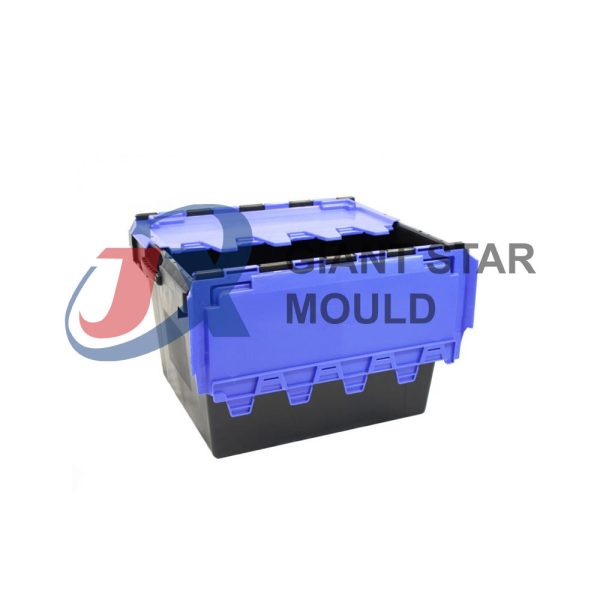
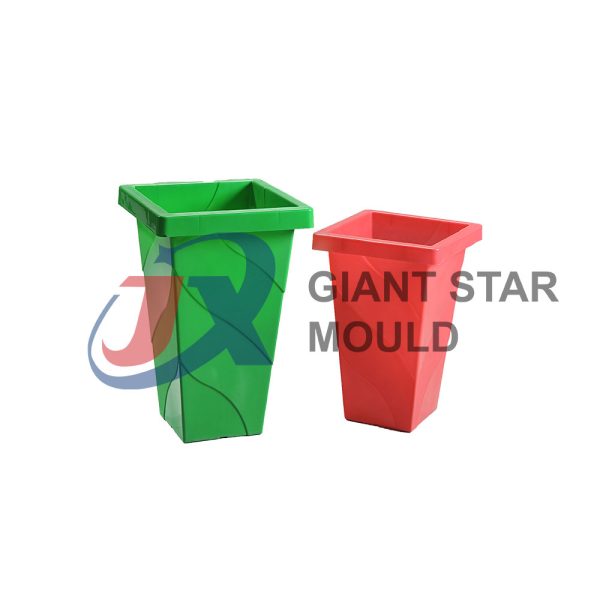
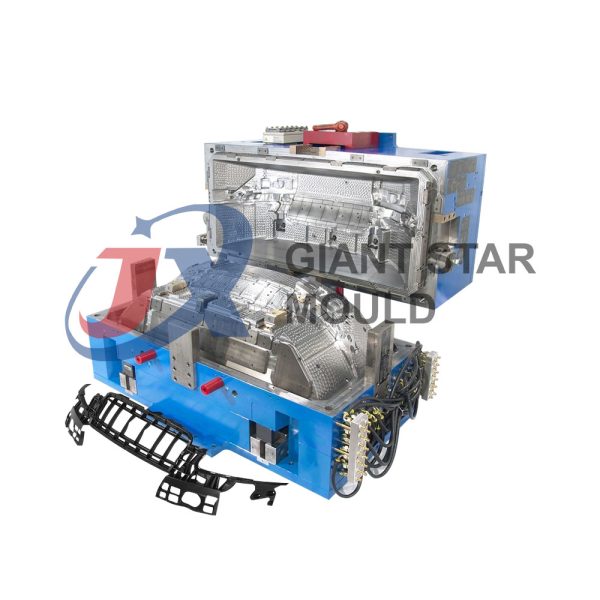
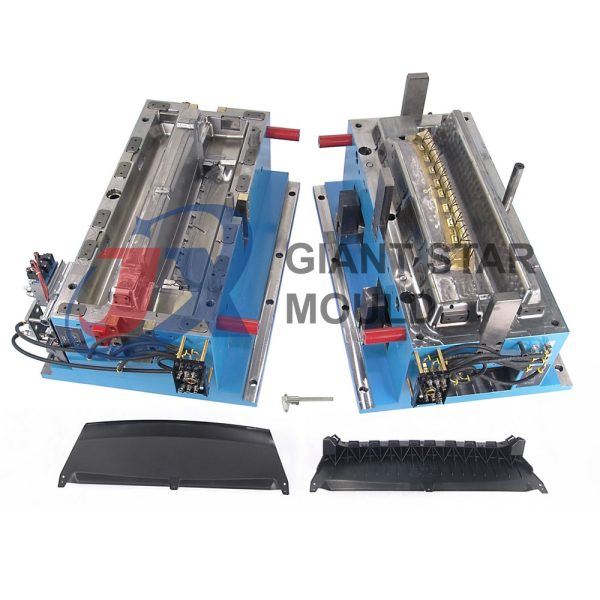
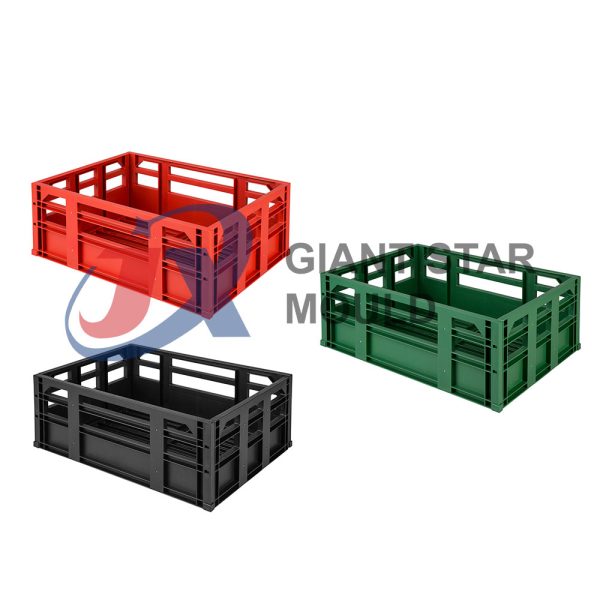
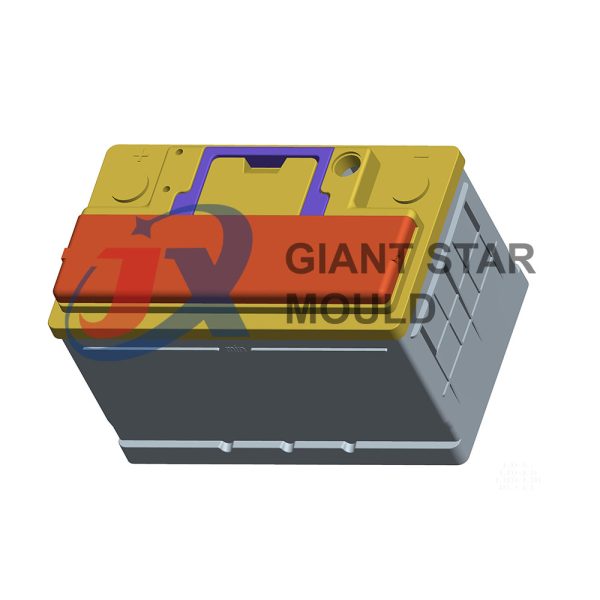
Battery Container Mould 31
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
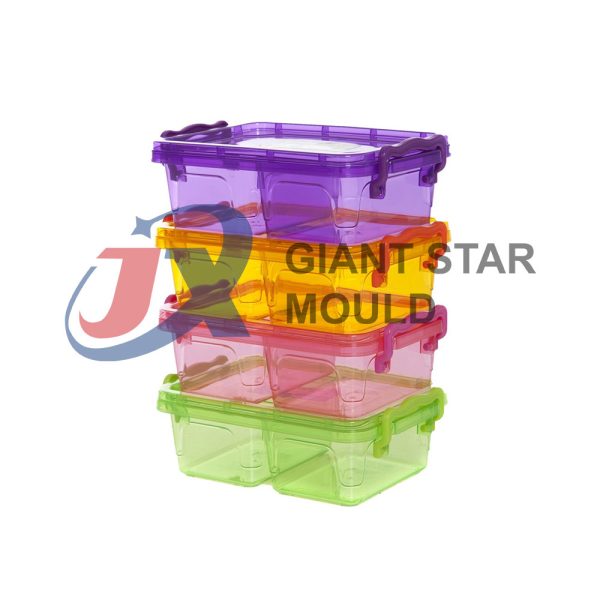
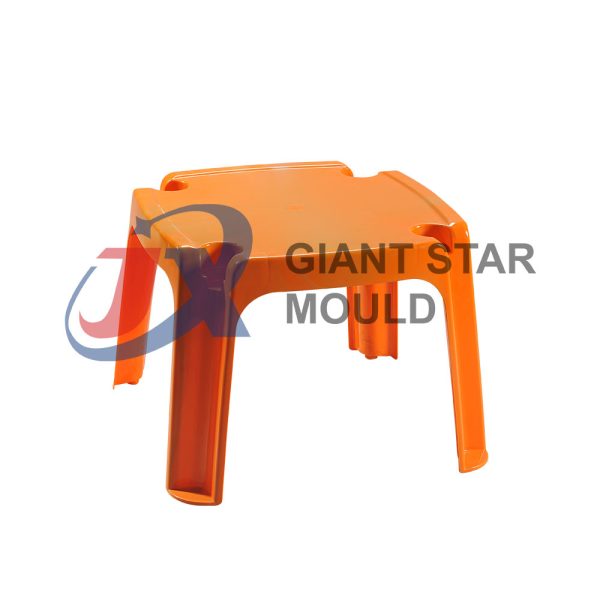
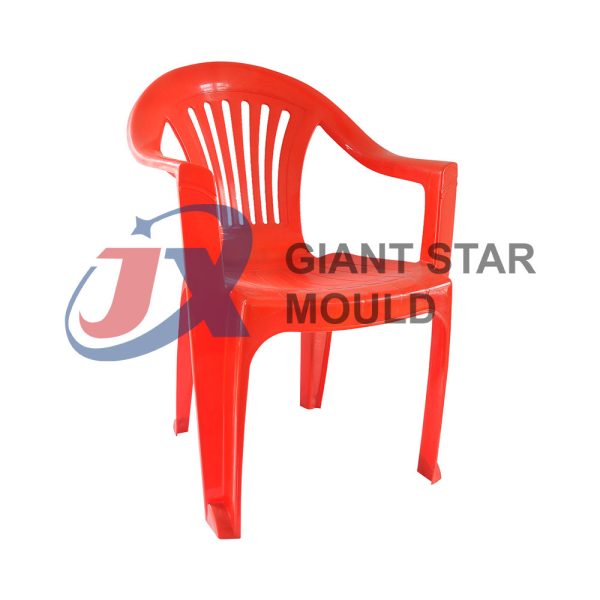
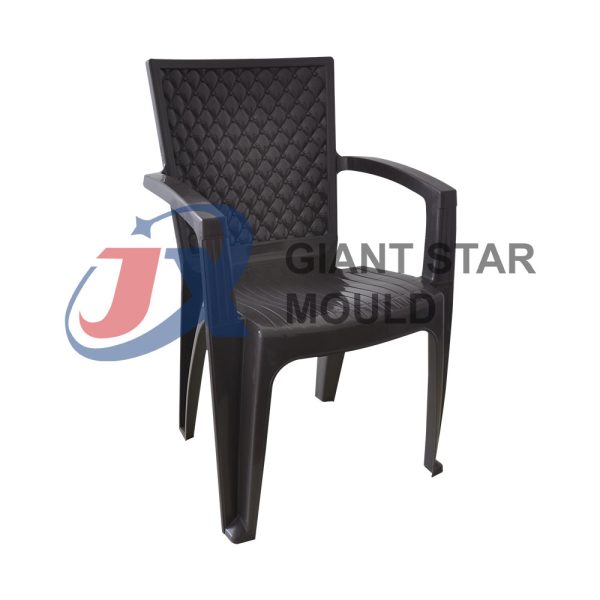
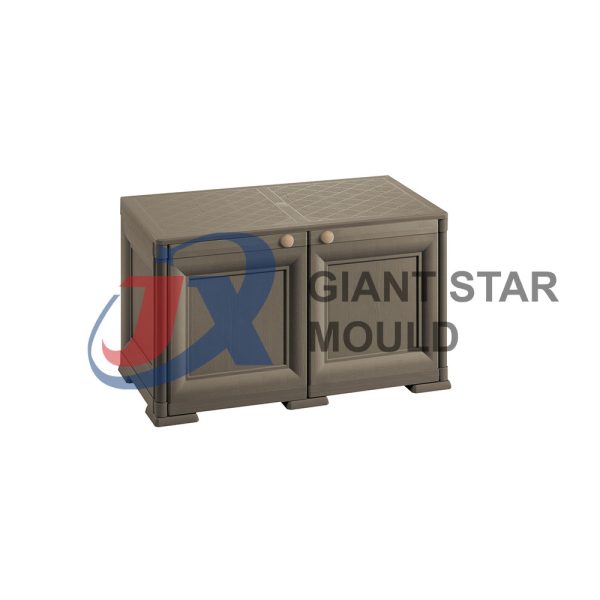
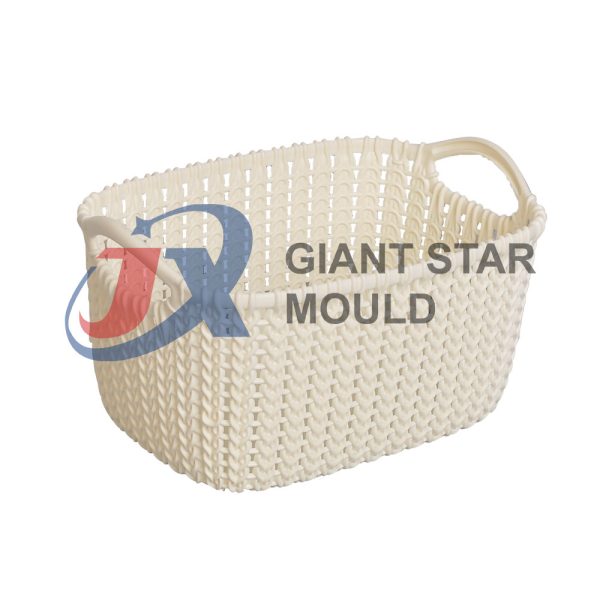
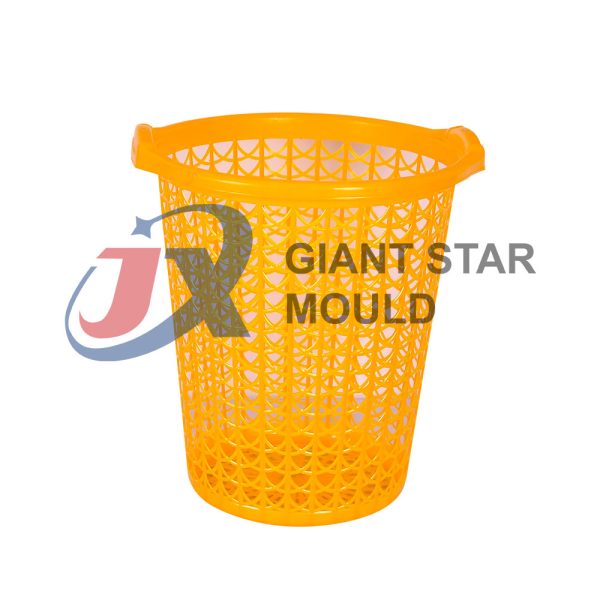
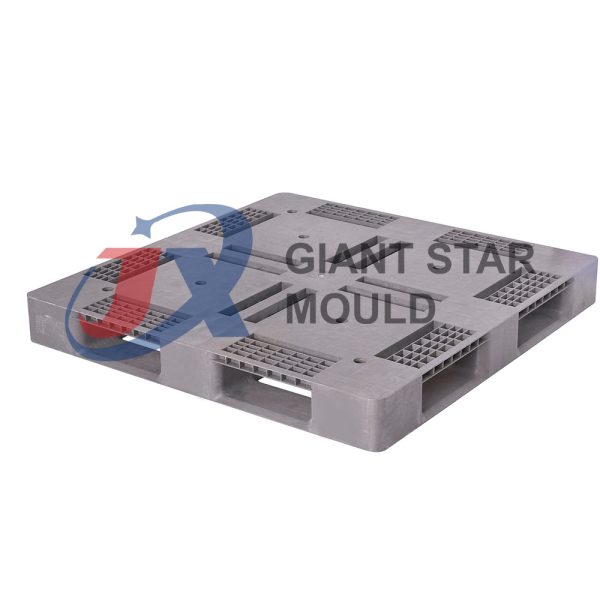
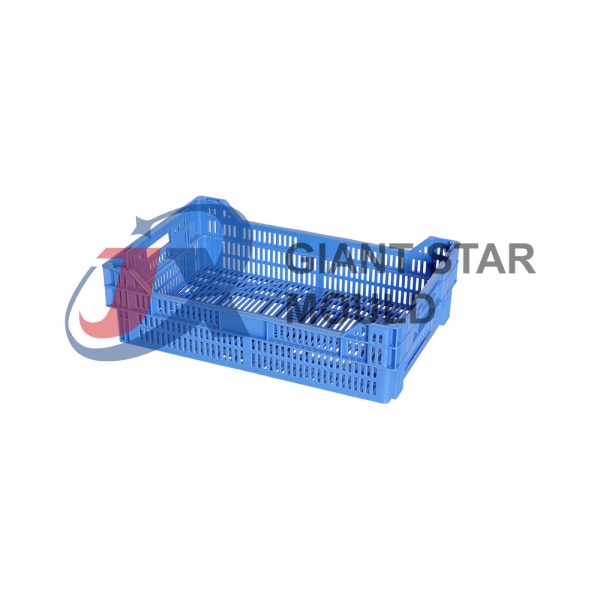
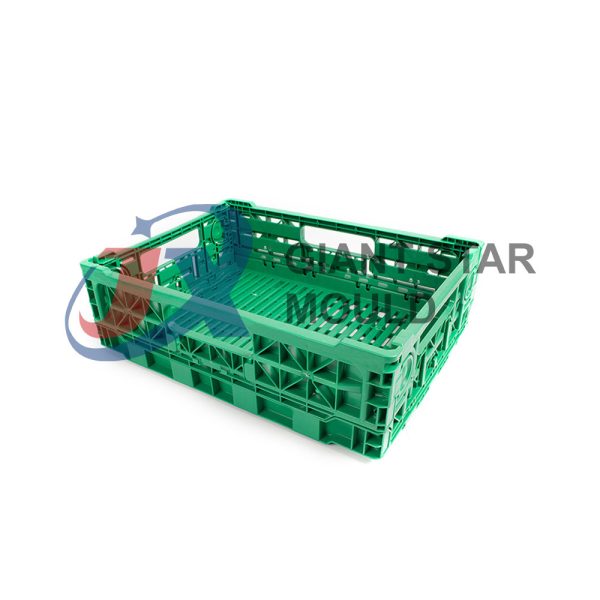
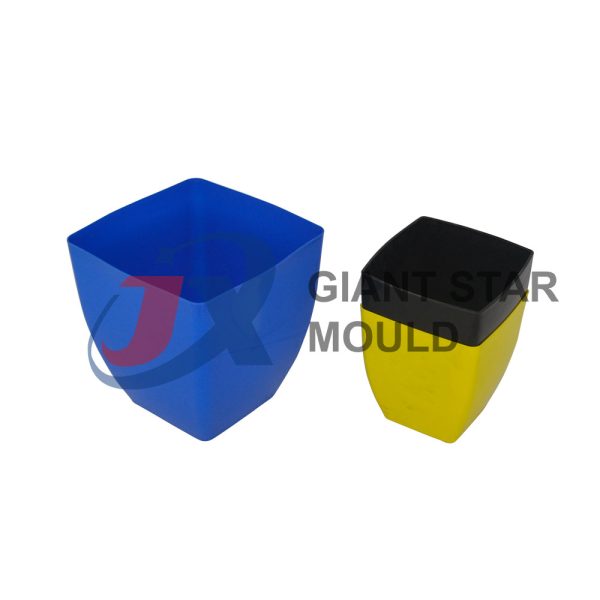
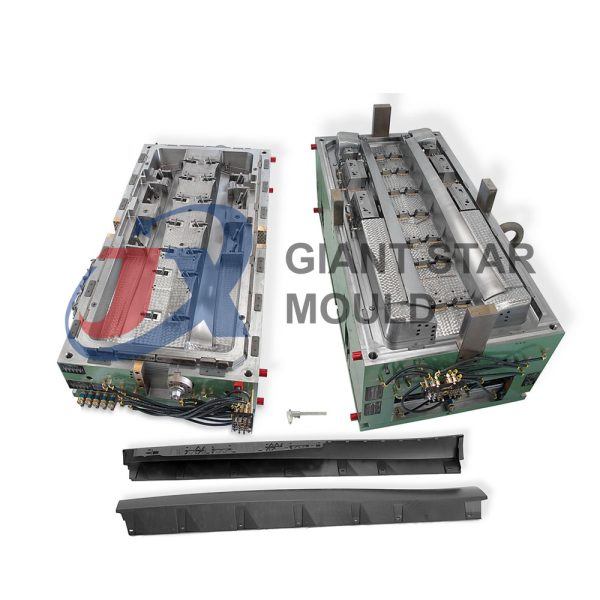
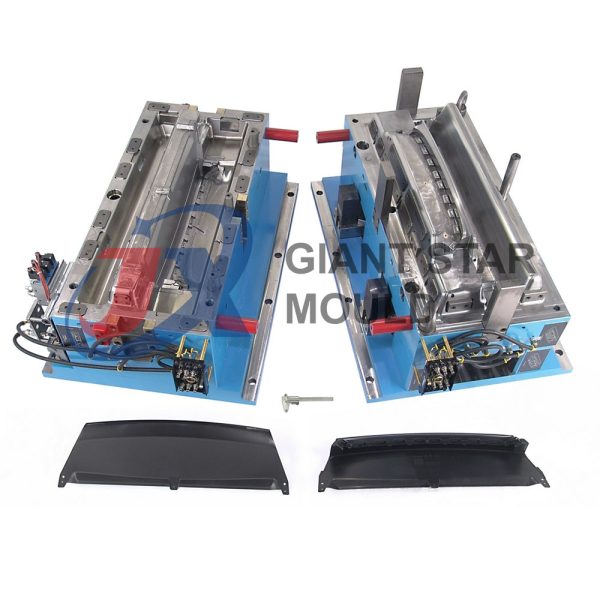
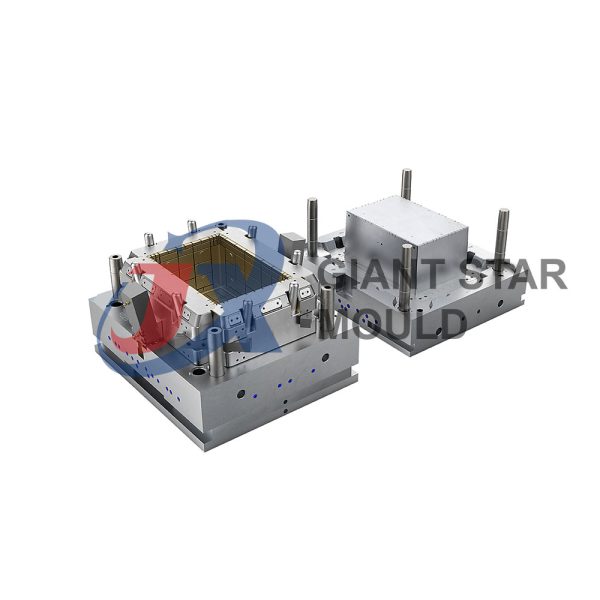
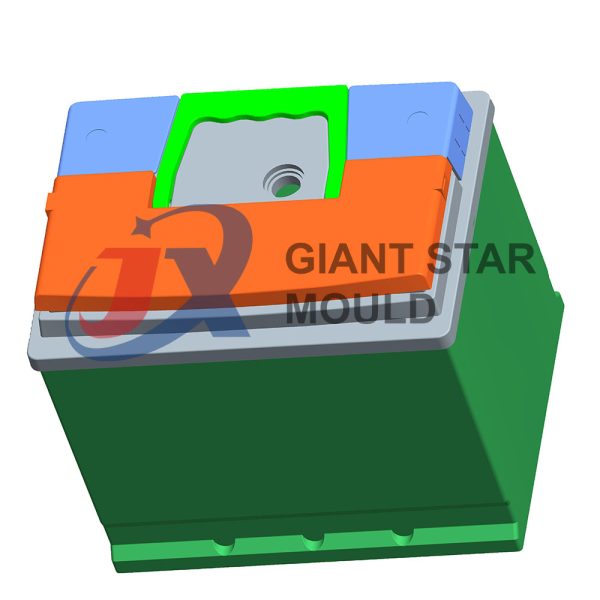
Battery Container Mould 30
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
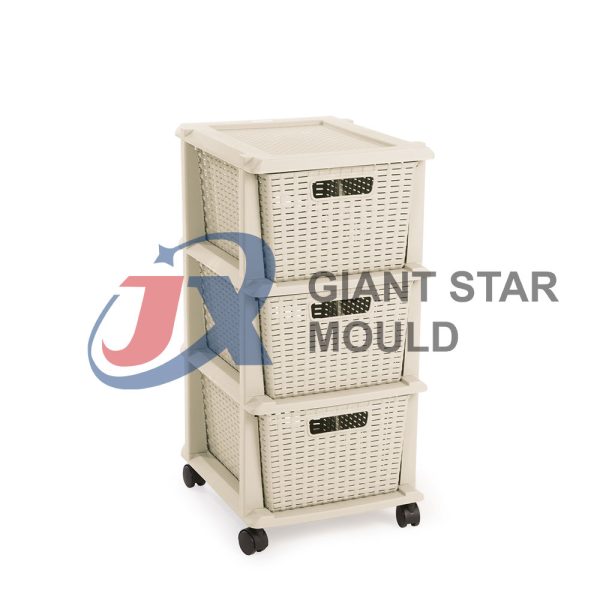
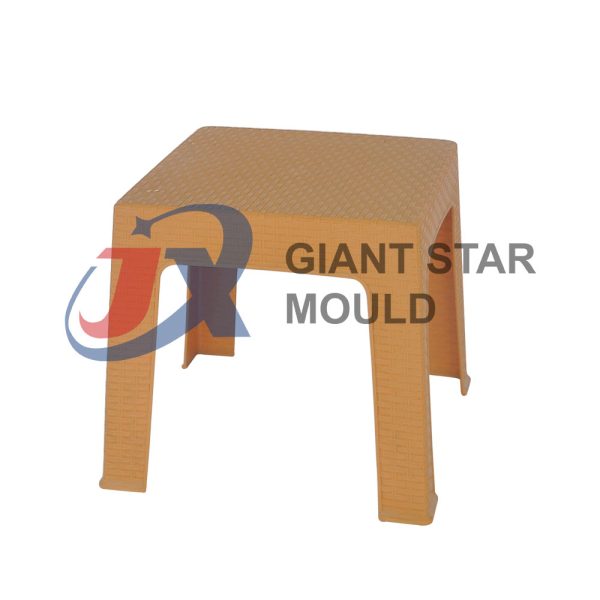
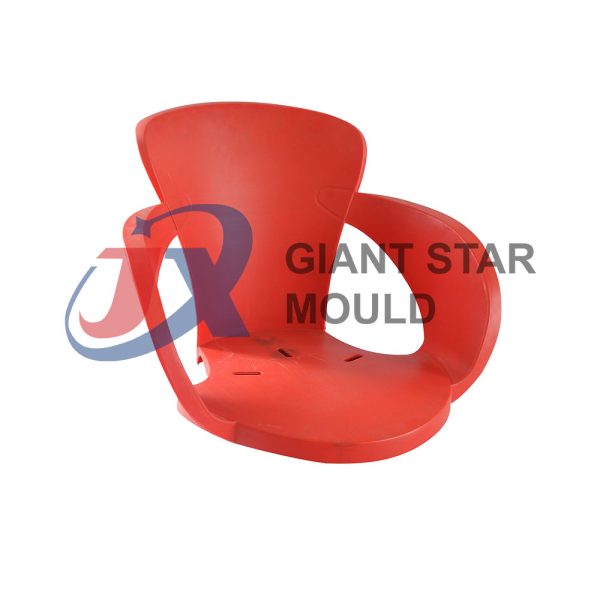
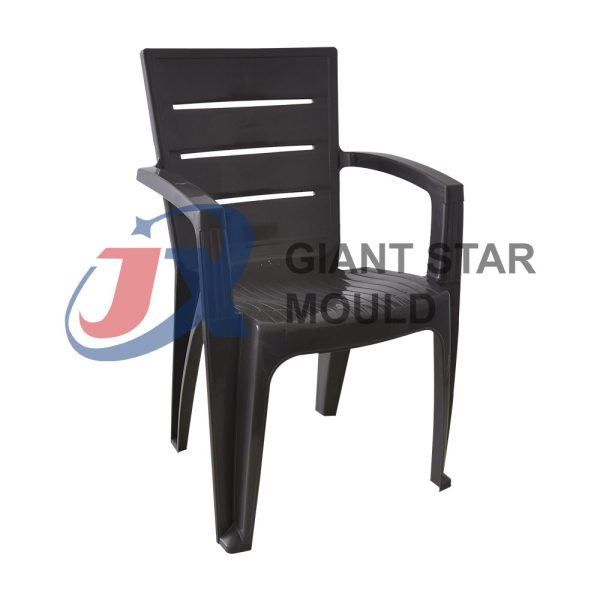
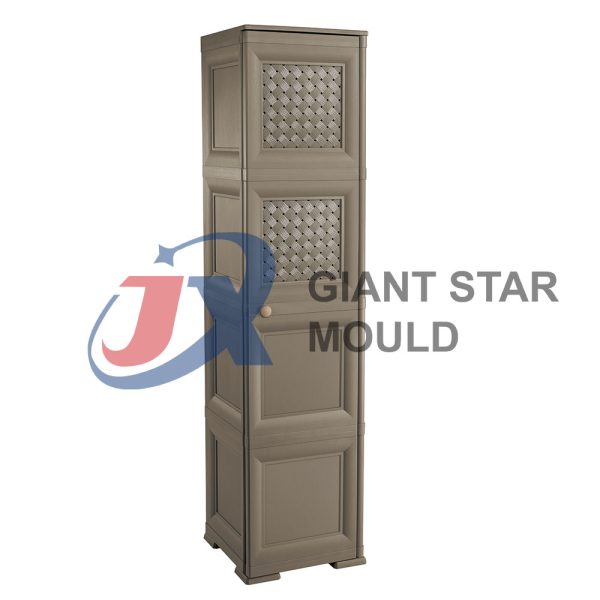
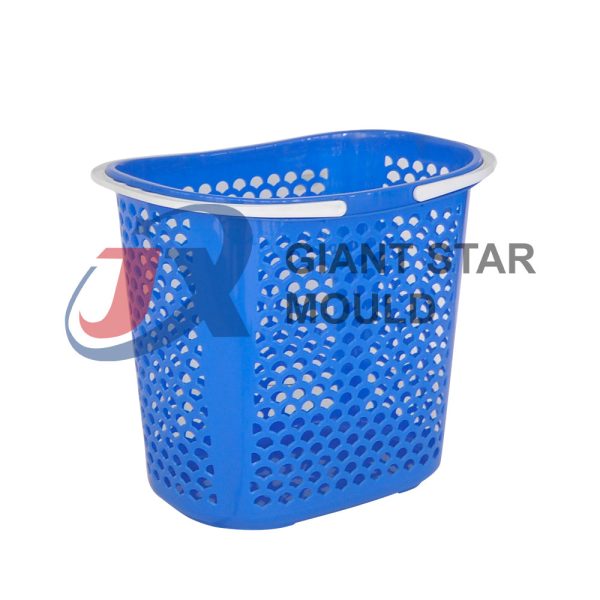
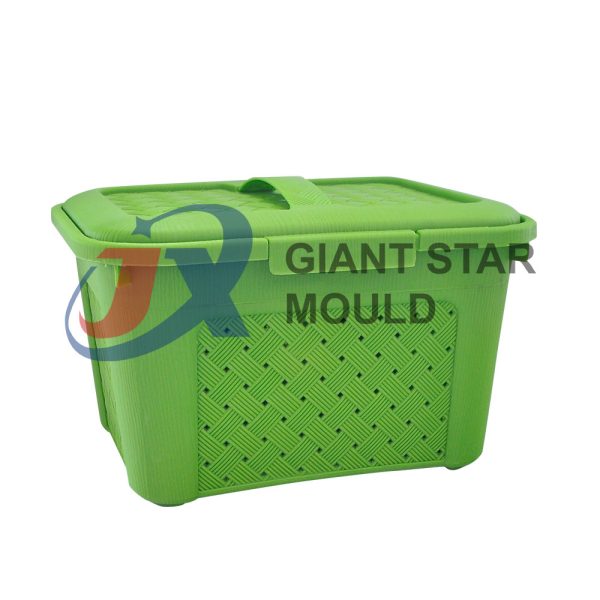
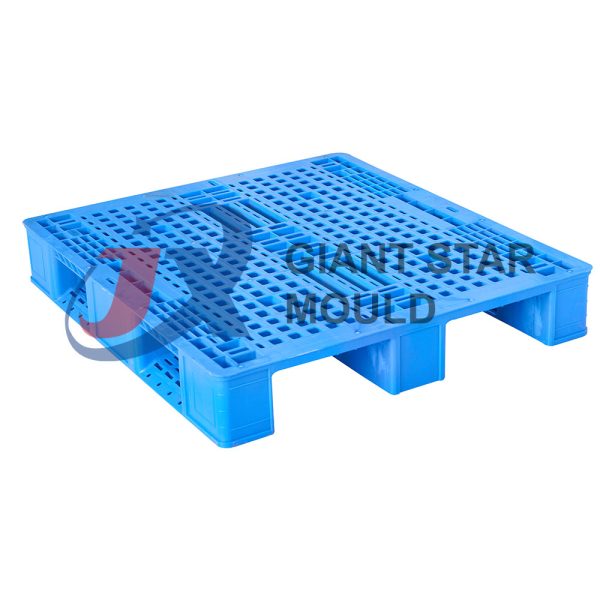
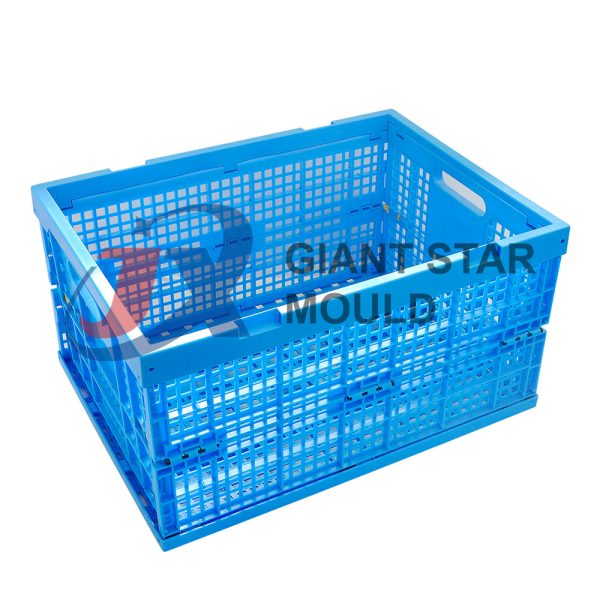
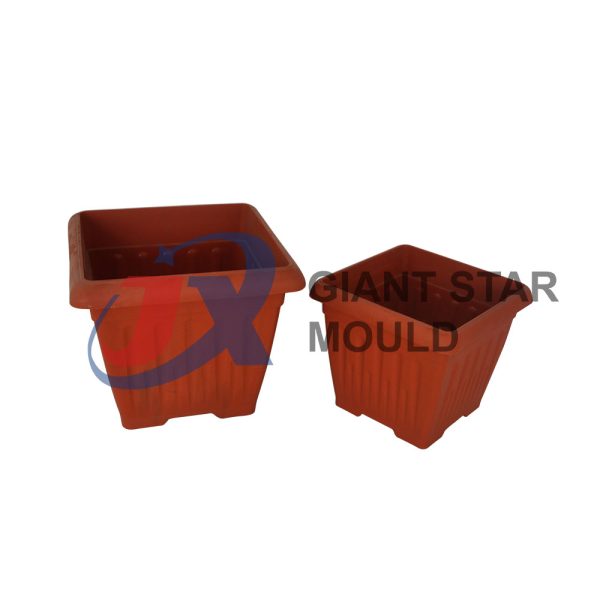
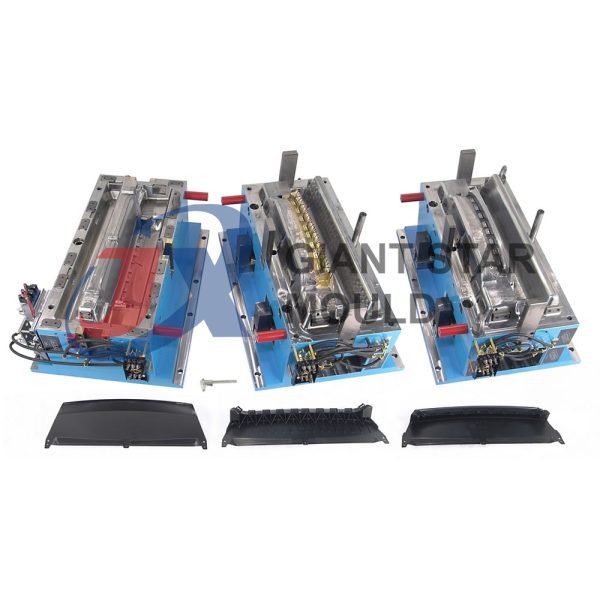
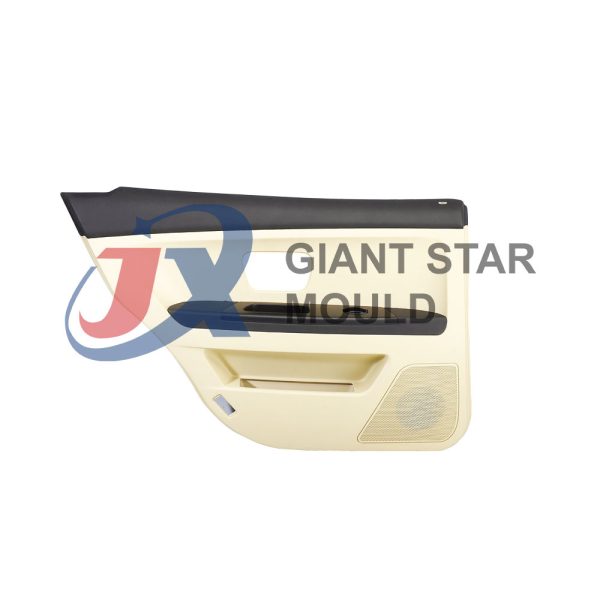
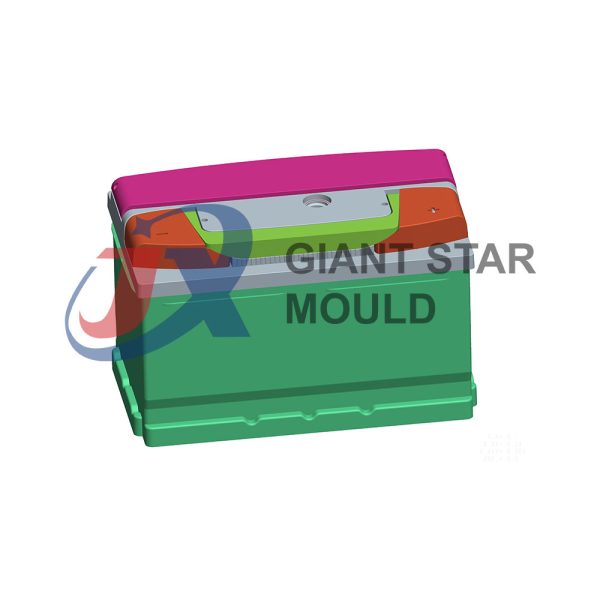
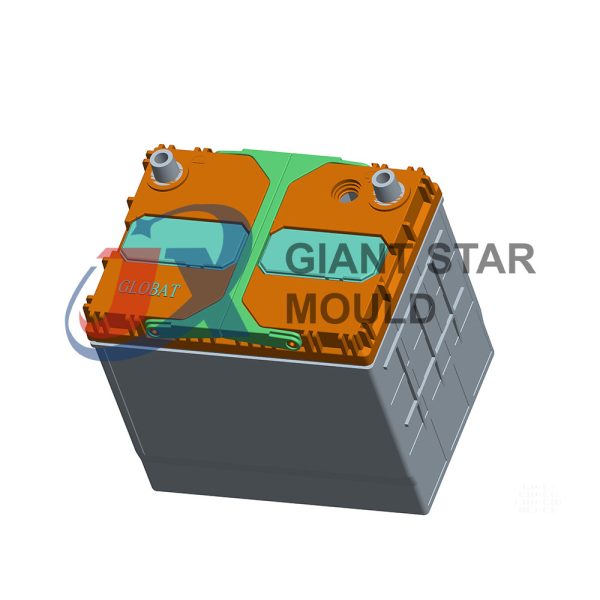
Battery Container Mould 29
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 28
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 27
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 26
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 25
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 24
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 23
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 22
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 21
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 20
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 19
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 18
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 17
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 16
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 15
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 14
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 13
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 12
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 11
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 10
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 09
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 08
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 07
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 06
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 05
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 04
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 03
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 02
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
Battery Container Mould 01
Creating a plastic battery container mold involves several steps and considerations. Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Design: Begin with the design of the battery container. This can be done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design should consider factors such as size, shape, material thickness, and any features required for assembly or functionality.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate plastic material for the battery container. Factors such as chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and cost should be taken into account.
- Mold Design: Once the container design is finalized, the mold design process begins. This involves designing the mold cavity, cores, runners, gates, and cooling channels. Mold design can also be done using CAD software, and it's crucial to ensure that the mold design allows for proper filling and cooling of the plastic material.
- Mold Fabrication: With the mold design complete, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This can be done through various methods such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), or casting. The choice of method depends on factors such as complexity, tolerances, and budget.
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is fabricated, it's installed into an injection molding machine. Plastic pellets are fed into the machine's hopper, melted, and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material fills the cavity, taking the shape of the battery container.
- Cooling and Ejection: After the plastic material is injected into the mold, it needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help facilitate this process. Once the plastic is sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the newly formed battery container is ejected.
- Trimming and Finishing: The ejected battery container may have excess material or rough edges that need to be trimmed or finished. This can be done manually or using automated trimming equipment.
- Quality Control: Finally, the battery containers undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspection, and testing for structural integrity.
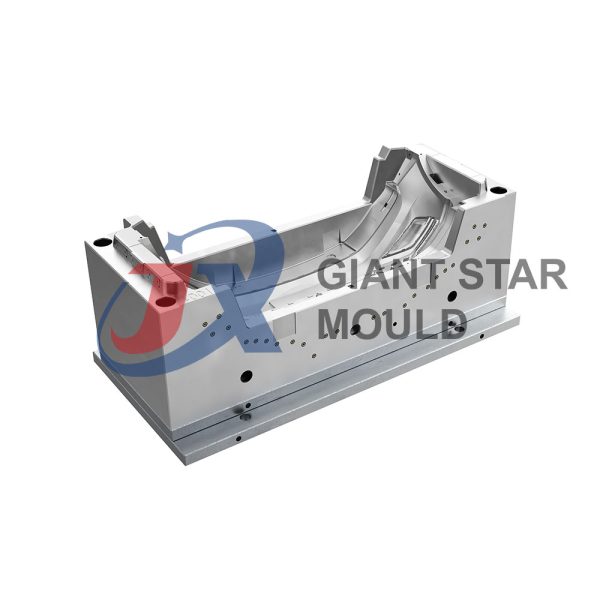
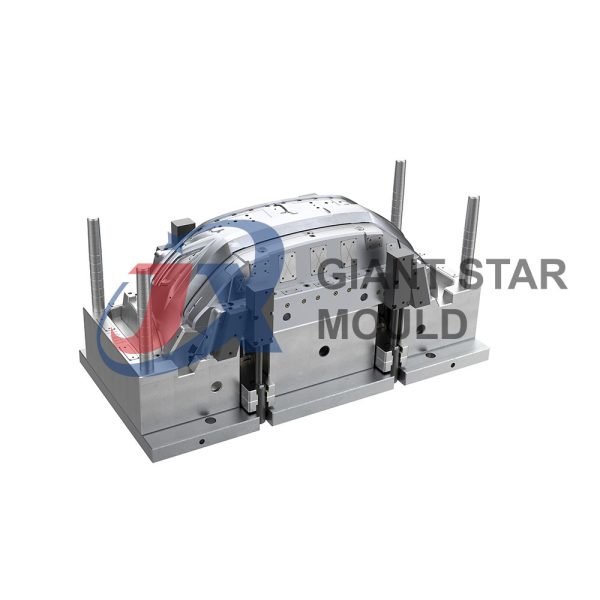
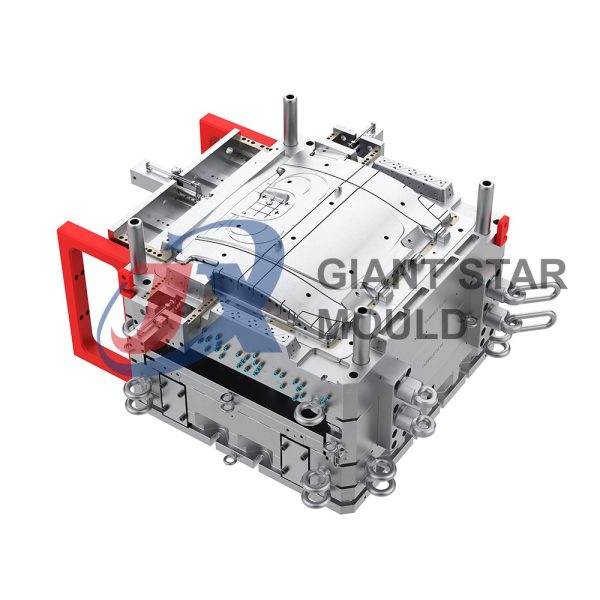
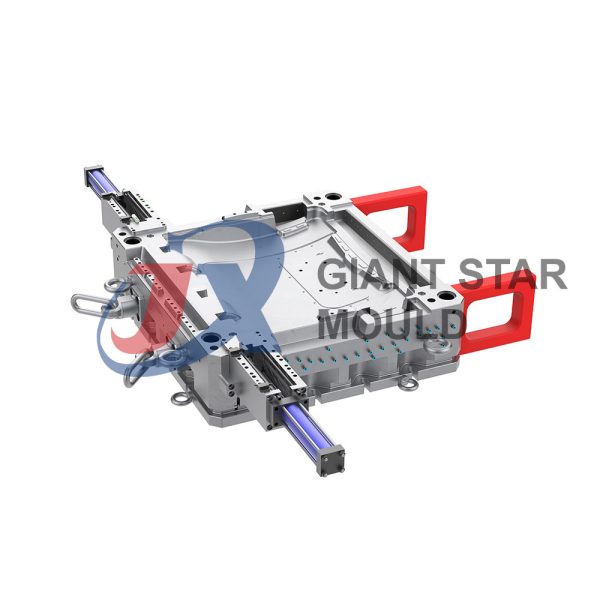
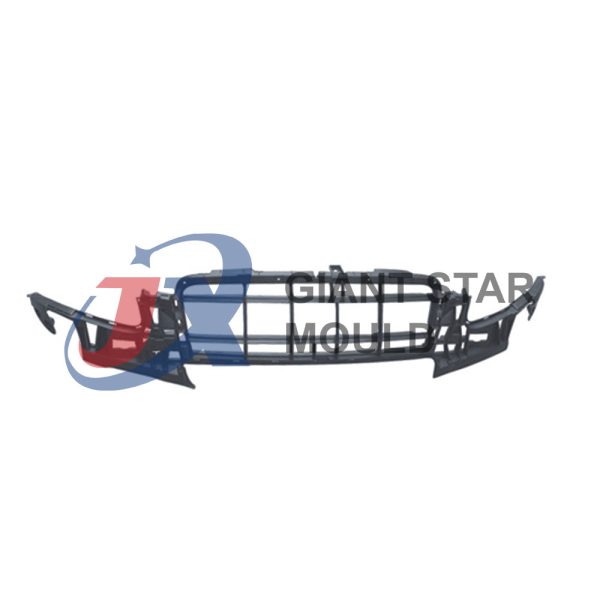
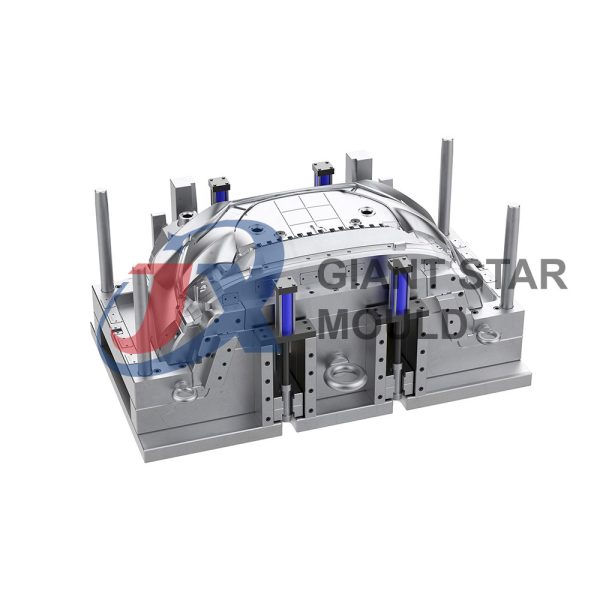
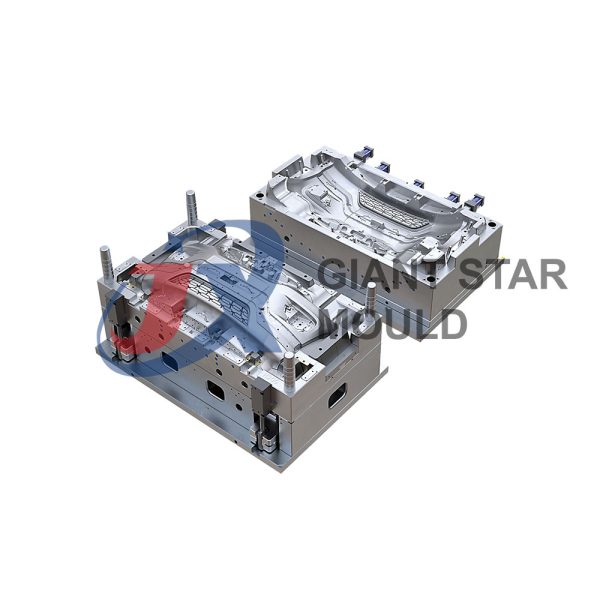
Automotive Mould 32
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 31
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 30
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 29
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 28
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 27
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 26
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 25
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 24
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 23
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 22
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 21
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 20
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 19
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 18
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 17
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 16
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 15
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 14
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 13
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 12
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 11
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 10
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 09
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 08
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 07
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 06
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 05
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 04
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 03
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 02
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production
Automotive Mould 01
Giant star Mold is a professional maker for automotive molds, car molds, automobile molds and vehicle molds in China. Our services include prototyping, tooling, sampling, pilot run, mass production and assembly.
For automotive mold maker, we often give you this suggestion:
Core and cavity steel: Up to customer’s budget and productivity required, we suggest the following steel grade: Pre- harden steel : P20 (1.2311), P20+Ni…etc Harfen Steel : H13 (1.2344) / NAK80…etc. Stainless steel : ASSAB Stavax…etc
Steel of Mold Base:Up to customer’s budget and requirement , we suggest different mold base steel to clients. Normal used material S50C, or P20
Hardness of Cavity & Core:Pre-Hardenss Steel : HRC 30~32+-1* Heat Treatment Steel : HRC 50~52+-1*
Core pulling or Ejection system: Depends on the Products. Commonly used :Motor , oil cylinder, stripping plate, angel pin, ejector pin…etc
Mold Accessories: Compatible to DME/ HASCO Standard.
Cooling System:In Core : Baffle or By pass cooling ;In Cavity Plate: Chain drilling type cooling
Surface Finish: Up to the product’s requirement, Normal used : Texture, EDM machining , Polishing
Mold Life: Up to mold steel grade, under ideal operation condition, 1. Pre-harden steel, min. 20~300000 shots 2. Harden / heat treatment steel : 60~800000 shots. 3. Stainless steel : 1 million shots.
Runner: 1. Cold runner 2. Hot runner 3.cold runner +hot runner
Delivery time: 80~90 days , presenting T1 samples
Packing: Standard Wooden Case
Production: We can also provide Pilot Run production and molding production